Page 26 - DLIS105_REFERENCE_SOURCES_AND_SERVICES
P. 26
Unit 1: Reference and Information Sources
Tertiary sources consist of information which is a distillation and collection of primary and secondary Notes
sources.
This is the most problematic category of all. Fortunately, you will rarely be expected to differentiate
between secondary and tertiary sources.
Some Definitions of Tertiary Sources:
• works which list primary and secondary resources in a specific subject area
• works which index, organize and compile citations to, and show you how to use, secondary
(and sometimes primary) sources
• materials in which the information from secondary sources has been “digested”-reformatted
and condensed, to put it into a convenient, easy-to-read form
• Sources which are once removed in time from secondary sources.
Some examples of tertiary sources:
• almanacs and fact books
• bibliographies (may also be secondary)
• chronologies
• dictionaries and encyclopedias (may also be secondary)
• directories
• guidebooks, manuals, etc.
• handbooks and data compilations (may also be secondary)
• indexing and abstracting tools used to locate primary and secondary sources (may also be
secondary)
• textbooks (may also be secondary).
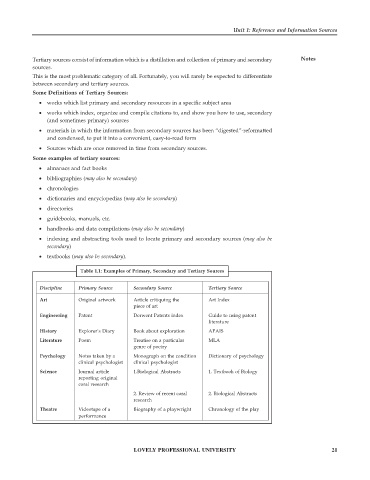
Table 1.1: Examples of Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sources
Discipline Primary Source Secondary Source Tertiary Source
Art Original artwork Article critiquing the Art Index
piece of art
Engineering Patent Derwent Patents index Guide to using patent
literature
History Explorer’s Diary Book about exploration APAIS
Literature Poem Treatise on a particular MLA
genre of poetry
Psychology Notes taken by a Monograph on the condition Dictionary of psychology
clinical psychologist clinical psychologist
Science Journal article 1.Biological Abstracts 1. Textbook of Biology
reporting original
coral research
2. Review of recent coral 2. Biological Abstracts
research
Theatre Videotape of a Biography of a playwright Chronology of the play
performance
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 21