Page 14 - DLIS006_INFORMATION SOURCES AND SERVICES
P. 14
Unit 1: Documentary Sources of Information
(i) Primary: The primary documents exist of their own and usually contain original Notes
information on the first formulation of any new observation, experiment, ideas, etc.
Thus, according to C. W. Hanson, a monograph, an article in periodical, text book,
and encyclopaedia are all primary documents. An article in encyclopaedia or text
book may not contain any new information on the subject but it presents the
information in the particular form for the first time. The articles concerned are not
a condensation or rewriting in any way of any existing document but has been
written specifically for the text book or the encyclopaedia.
(ii) Secondary: All secondary publications present the contents of primary document in
a condensed form or list them in a helpful way so that the existence of a primary
document can be known and access to it can be made.
(iii) Primary/Secondary Sources of Information: Conference proceedings, theses and
dissertations, monographs, etc. have the characteristics of both primary and
secondary sources of information. Those of documents representing new facts can
be regarded as primary publication and those having the character of reviews can be
grouped as secondary publication. As a result of such mixing of primary and
secondary sources of information some expert doesn’t consider this division to be
much practical utility.
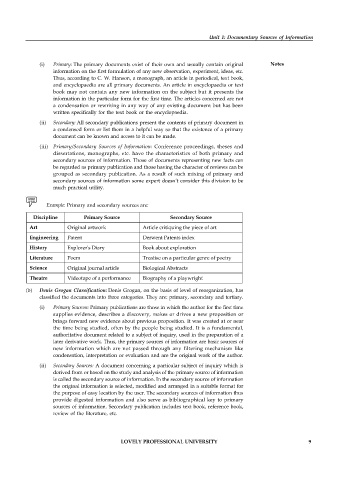
Example: Primary and secondary sources are:
Discipline Primary Source Secondary Source
Art Original artwork Article critiquing the piece of art
Engineering Patent Derwent Patents index
History Explorer's Diary Book about exploration
Literature Poem Treatise on a particular genre of poetry
Science Original journal article Biological Abstracts
Theatre Videotape of a performance Biography of a playwright
(b) Denis Grogan Classification: Denis Grogan, on the basis of level of reorganization, has
classified the documents into three categories. They are: primary, secondary and tertiary.
(i) Primary Sources: Primary publications are those in which the author for the first time
supplies evidence, describes a discovery, makes or drives a new proposition or
brings forward new evidence about previous proposition. It was created at or near
the time being studied, often by the people being studied. It is a fundamental,
authoritative document related to a subject of inquiry, used in the preparation of a
later derivative work. Thus, the primary sources of information are basic sources of
new information which are not passed through any filtering mechanism like
condensation, interpretation or evaluation and are the original work of the author.
(ii) Secondary Sources: A document concerning a particular subject of inquiry which is
derived from or based on the study and analysis of the primary source of information
is called the secondary source of information. In the secondary source of information
the original information is selected, modified and arranged in a suitable format for
the purpose of easy location by the user. The secondary sources of information thus
provide digested information and also serve as bibliographical key to primary
sources of information. Secondary publication includes text book, reference book,
review of the literature, etc.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9