Page 133 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 133
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes The 802.3af Ethernet standard allowing both DC power and digital data to be communicated
over the pairs of wires.
6.5 Wireless Networks
Wireless network refers to any type of computer network that is not connected by cables of any
kind. It is a method by which telecommunications networks and enterprise (business), installations
avoid the costly process of introducing cables into to a building, or as a connection between
various equipment locations. Wireless telecommunications networks are generally implemented
and administered using a transmission system called radio waves. This implementation takes
place at the physical level, (layer), of the network structure.
6.5.1 Types of Wireless Connections
6.5.1.1 Wireless PAN
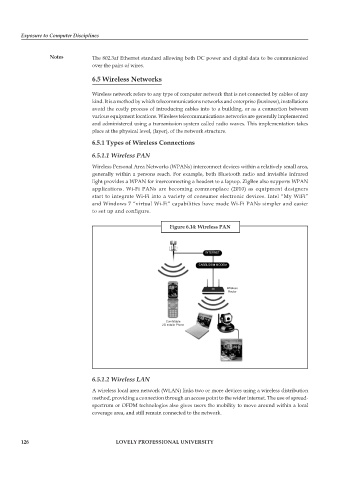
Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) interconnect devices within a relatively small area,
generally within a persons reach. For example, both Bluetooth radio and invisible Infrared
light provides a WPAN for interconnecting a headset to a laptop. ZigBee also supports WPAN
applications. Wi-Fi PANs are becoming commonplace (2010) as equipment designers
start to integrate Wi-Fi into a variety of consumer electronic devices. Intel “My WiFi”
and Windows 7 “virtual Wi-Fi” capabilities have made Wi-Fi PANs simpler and easier
to set up and configure.
Figure 6.14: Wireless PAN
INTERNET
CABEL/DSM MODEM
Wireless
Router
Comfatable
2G mobile Phone
6.5.1.2 Wireless LAN
A wireless local area network (WLAN) links two or more devices using a wireless distribution
method, providing a connection through an access point to the wider internet. The use of spread-
spectrum or OFDM technologies also gives users the mobility to move around within a local
coverage area, and still remain connected to the network.
126 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY