Page 33 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 33
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes (i) Special purpose registers ( SPRs): Its hold program state; they usually include the program
counter (aka instruction pointer), stack pointer, and status register (aka processor status
word). In embedded microprocessors, they can also correspond to specialized hardware
elements.
(j) Instruction registers: Its store the instruction currently being executed.
(k) In some architectures, model-specific registers (also called machine-specific registers) store
data and settings related to the processor itself. Because their meanings are attached to
the design of a specific processor, they cannot be expected to remain standard between
processor generations.
(l) Control and status registers: It has three types—Program counter, instruction registers,
Program status word (PSW).
(m) Registers related to fetching information from RAM, a collection of storage registers located
on separate chips from the CPU (unlike most of the above, these are generally not architectural
registers):
• Memory buffer register
• Memory data register
• Memory address register
• Memory Type Range Registers (MTRR)
Hardware registers are similar, but occur outside CPUs.
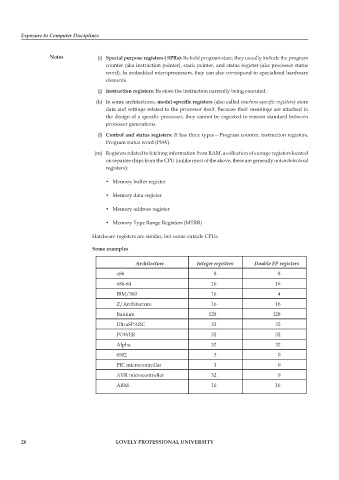
Some examples
Architecture Integer registers Double FP registers
x86 8 8
x86-64 16 16
IBM/360 16 4
Z/Architecture 16 16
Itanium 128 128
UltraSPARC 32 32
POWER 32 32
Alpha 32 32
6502 3 0
PIC microcontroller 1 0
AVR microcontroller 32 0
ARM 16 16
26 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY