Page 87 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 87
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes 5.1.2 OSI Model
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network architecture, developed by International
Organization for Standardization, is an open standard for communication in the network across
different equipment and applications by different vendors. Though not widely deployed, the OSI
7 layer model is considered the primary network architectural model for inter-computing and
inter-networking communications.
In addition to the OSI network architecture model, there exist other network architecture models by
many vendors, such as IBM SNA (Systems Network Architecture), Digital Equipment Corporation
(DEC; now part of HP) DNA (Digital Network Architecture), Apple computers AppleTalk, and
Novells NetWare.
Network architecture provides only a conceptual framework for communications between
computers. The model itself does not provide specific methods of communication. Actual
communication is defined by various communication protocols.
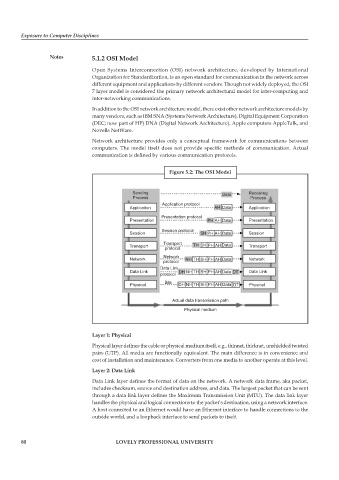
Figure 5.2: The OSI Model
Sending Data Receiving
Process Process
Application protocol
Application AH Data Application
Presentation protocol
Presentation PH AH Data Presentation
Session protocol
Session SH PH AH Data Session
Transport
Transport TH SH PH AH Data Transport
protocol
Network
Network NH TH SH PH AH Data Network
protocol
Data Link
Data Link DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT Data Link
protocol
Bits
Physical DH NH TH SH PH AH Data DT Physical
Actual data transmission path
Physical medium
Layer 1: Physical
Physical layer defines the cable or physical medium itself, e.g., thinnet, thicknet, unshielded twisted
pairs (UTP). All media are functionally equivalent. The main difference is in convenience and
cost of installation and maintenance. Converters from one media to another operate at this level.
Layer 2: Data Link
Data Link layer defines the format of data on the network. A network data frame, aka packet,
includes checksum, source and destination address, and data. The largest packet that can be sent
through a data link layer defines the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU). The data link layer
handles the physical and logical connections to the packet’s destination, using a network interface.
A host connected to an Ethernet would have an Ethernet interface to handle connections to the
outside world, and a loopback interface to send packets to itself.
80 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY