Page 35 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 35
Quantitative Techniques – I
Notes
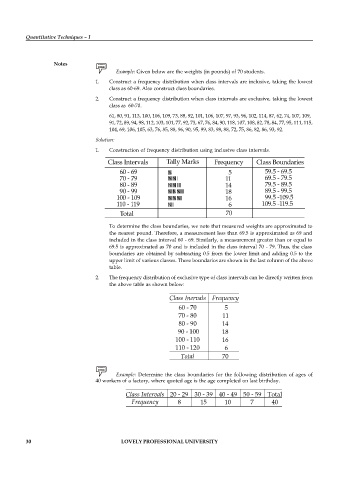
Example: Given below are the weights (in pounds) of 70 students.
1. Construct a frequency distribution when class intervals are inclusive, taking the lowest
class as 60-69. Also construct class boundaries.
2. Construct a frequency distribution when class intervals are exclusive, taking the lowest
class as 60-70.
61, 80, 91, 113, 100, 106, 109, 73, 88, 92, 101, 106, 107, 97, 93, 96, 102, 114, 87, 62, 74, 107, 109,
91, 72, 89, 94, 98, 112, 103, 101, 77, 92, 73, 67, 76, 84, 90, 118, 107, 108, 82, 78, 84, 77, 95, 111, 115,
104, 69, 106, 105, 63, 76, 85, 88, 96, 90, 95, 99, 83, 98, 88, 72, 75, 86, 82, 86, 93, 92.
Solution:
1. Construction of frequency distribution using inclusive class intervals.
To determine the class boundaries, we note that measured weights are approximated to
the nearest pound. Therefore, a measurement less than 69.5 is approximated as 69 and
included in the class interval 60 - 69. Similarly, a measurement greater than or equal to
69.5 is approximated as 70 and is included in the class interval 70 - 79. Thus, the class
boundaries are obtained by subtracting 0.5 from the lower limit and adding 0.5 to the
upper limit of various classes. These boundaries are shown in the last column of the above
table.
2. The frequency distribution of exclusive type of class intervals can be directly written from
the above table as shown below:
60 - 70 5
70 - 80 11
80 - 90 14
90 - 100 18
100 - 110 16
110 - 120 6
70
Example: Determine the class boundaries for the following distribution of ages of
40 workers of a factory, where quoted age is the age completed on last birthday.
20 - 29 30 - 39 40 - 49 50 - 59 Total
8 15 10 7 40
30 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY