Page 200 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 200
Unit 13: Oligopoly
13.2 Types of Oligopoly Notes
There are two major types of oligopoly:
1. Non-collusive- Cournot Model (Duopoly) and Kinked Demand Curve Models
2. Collusive- Joint Profit Maximisation and Price Leadership
We will discuss the models on one by one in the following subsections. However, we will discuss
the Kinked Demand Curve Models separately in the next section.
13.2.1 Cournot Model (Duopoly)
The Cournot model (by Antoine Cournot, 1838) is in terms of duopoly (two sellers) but it can be
easily extended to an oligopolistic situation. This model analyses the process of equilibrium in a
duopoly situation when each duopolist assumes that his rival will not react when he changes his
output to maximise profits. The assumptions of this model are:
1. There are two sellers in the market.
2. The products sold by these two sellers are homogeneous.
3. The market, or total demand curve, is known and it is a straight line.
4. Each duopolist assumes that his rival’s output will remain constant when he changes his
output. Thus, each duopolist assumes his rival will not react to his action. This is, for
each duopolist the conjectural variation or seller interdependence, as given by dQ /dQ or
1 2
dQ /dQ , is assumed to be zero. (Q and Q are the outputs of two sellers).
1
2
1
2
5. Each duopolist produces output of which the profits are at the maximum.
6. The cost of production is zero for both the sellers.
Example: Two natural springs of mineral water with healing qualities, are each
owned by one seller. The average and marginal costs for each seller are zero and these
curves coincide with the X-axis.
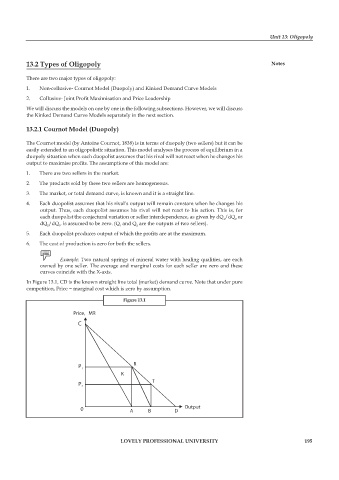
In Figure 13.1, CD is the known straight line total (market) demand curve. Note that under pure
competition, Price = marginal cost which is zero by assumption.
Figure 13.1
Price, MR
C
P 1 R
K
T
P 2
0 A B D Output
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 195