Page 4 - DSOC101_FUNDAMENTALS_OF_SOCIOLOGY_HINDI
P. 4
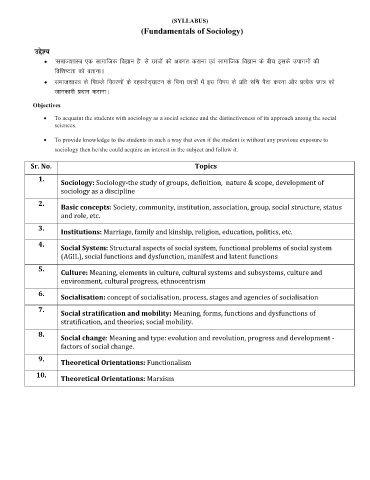
(SYLLABUS)
(Fundamentals of Sociology)
mís';
• ^lekt'kkL= ,d lkekftd foKku gS* ls Nk=ksa dks voxr djkuk ,oa lkekftd foKku ds chp blds mikxeksa dh
fof'k"Vrk dks crkukA
• lekt'kkL= ds fiNys fooj.kksa ds jgL;ksn~?kkVu ds fCkuk Nk=ksa esa bl fo"k; ds izfr #fp iSnk djuk vkSj izR;sd Nk= dks
tkudkjh iznku djkukA
Objectives
• To acquaint the students with sociology as a social science and the distinctiveness of its approach among the social
sciences.
• To provide knowledge to the students in such a way that even if the student is without any previous exposure to
sociology then he/she could acquire an interest in the subject and follow it.
Sr. No. Topics
1.
Sociology: Sociology-the study of groups, definition, nature & scope, development of
sociology as a discipline
2.
Basic concepts: Society, community, institution, association, group, social structure, status
and role, etc.
3.
Institutions: Marriage, family and kinship, religion, education, politics, etc.
4.
Social System: Structural aspects of social system, functional problems of social system
(AGIL), social functions and dysfunction, manifest and latent functions
5.
Culture: Meaning, elements in culture, cultural systems and subsystems, culture and
environment, cultural progress, ethnocentrism
6.
Socialisation: concept of socialisation, process, stages and agencies of socialisation
7.
Social stratification and mobility: Meaning, forms, functions and dysfunctions of
stratification, and theories; social mobility.
8.
Social change: Meaning and type: evolution and revolution, progress and development -
factors of social change.
9.
Theoretical Orientations: Functionalism
10.
Theoretical Orientations: Marxism