Page 36 - DCAP202_Fundamentals of Web Programming
P. 36
Unit 3: HTML Command and Structure
Notes
Example: <i>Your italics text goes here.</i>
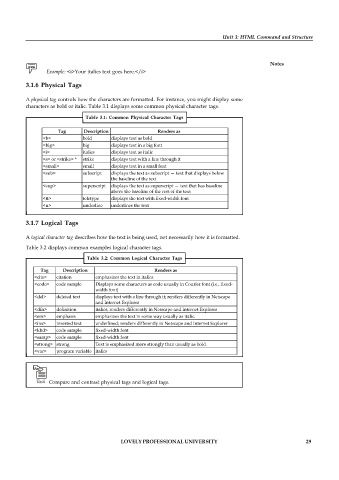
3.1.6 Physical Tags
A physical tag controls how the characters are formatted. For instance, you might display some
characters as bold or italic. Table 3.1 displays some common physical character tags.
Table 3.1: Common Physical Character Tags
Tag Description Renders as
<b> bold displays text as bold
<big> big displays text in a big font
<i> italics displays text as italic
<s> or <strike> * strike displays text with a line through it
<small> small displays text in a small font
<sub> subscript displays the text as subscript — text that displays below
the baseline of the text
<sup> superscript displays the text as superscript — text that has baseline
above the baseline of the rest of the text
<tt> teletype displays the text with fixed-width font
<u> underline underlines the text
3.1.7 Logical Tags
A logical character tag describes how the text is being used, not necessarily how it is formatted.
Table 3.2 displays common examples logical character tags.
Table 3.2: Common Logical Character Tags
Tag Description Renders as
<cite> citation emphasizes the text in italics.
<code> code sample Displays some characters as code usually in Courier font (i.e., fixed-
width font)
<del> deleted text displays text with a line through it; renders differently in Netscape
and Internet Explorer
<dfn> definition italics; renders differently in Netscape and Internet Explorer
<em> emphasis emphasizes the text in some way usually as italic.
<ins> inserted text underlined; renders differently in Netscape and Internet Explorer
<kbd> code sample fixed-width font
<samp> code sample fixed-width font
<strong> strong Text is emphasized more strongly than usually as bold.
<var> program variable italics
Task Compare and contrast physical tags and logical tags.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 29