Page 167 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 167
Management of Finances
Notes ability to use fixed financial charges to magnify the effects of charge in EBIT/operating
profit on firm’s earnings per share.
3. Total leverage is concerned with the relationship between the firm’s sales revenue and
EPS.
7.1 Operating Leverage
Operating leverage results from the existence of the fixed operating expenses in the firm’s
income stream. The operating costs of a firm fall into three categories:
1. Fixed costs, which may be defined as those do not vary with sales volume, are a function
of time and are typically contractual; they must be paid regardless of the amount of
revenue available with sales volume.
2. Variable costs, which vary directly.
3. Semi-variable or semi-fixed costs are those, which are partly fixed and partly variable.
They are fixed over a certain higher sales volumes. Since the last category of cost can be
broken down into fixed and variable components, the cost of a firm in operational terms
can be divided into fixed and variables. The operating leverage occurs anytime a firm has
fixed costs that must be met regardless of the volume. With fixed costs, the percentage
change in profit accompanying a change in volume is greater than the percentage change
in volume.
Notes Operating leverage is defined as the firm’s ability to use fixed operating costs to
magnify effects of changes in sales or its earnings before interest on tax.
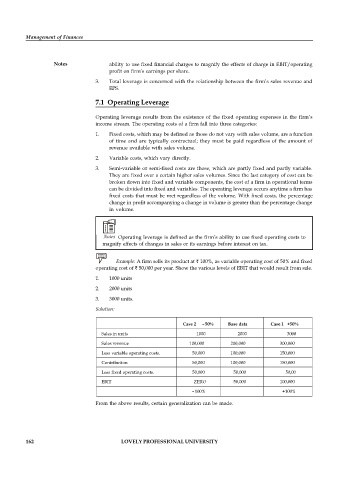
Example: A firm sells its product at 100%, as variable operating cost of 50% and fixed
operating cost of 50,000 per year. Show the various levels of EBIT that would result from sale.
1. 1000 units
2. 2000 units
3. 3000 units.
Solution:
Case 2 –50% Base data Case 1 +50%
Sales in units 1000 2000 3000
Sales revenue 100,000 200,000 300,000
Less variable operating costs. 50,000 100,000 150,000
Contribution 50,000 100,000 150,000
Less fixed operating costs. 50,000 50,000 50,00
EBIT ZERO 50,000 100,000
–100% +100%
From the above results, certain generalization can be made.
162 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY