Page 183 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 183
Management of Finances
Notes Solution:
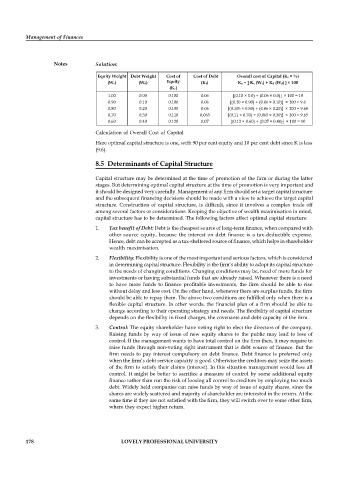
Equity Weight Debt Weight Cost of Cost of Debt Overall cost of Capital (Ko = %)
(We) (Wd) Equity (K Ko = [ Ke (We) + Kd (Wd) ] × 100
(Ke)
1.00 0.00 0.100 0.06 [(0.10 × 1.0) + (0.06 × 0.0)] × 100 = 10
0.90 0.10 0.100 0.06 [(0.10 × 0.90) + (0.06 × 0.10)] × 100 = 9.6
0.80 0.20 0.105 0.06 [(0.105 × 0.80) + (0.06 × 0.20)] × 100 = 9.68
0.70 0.30 0.110 0.065 [(0.11 × 0.70) + (0.065 × 0.30)] × 100 = 9.65
0.60 0.40 0.120 0.07 [(0.12 × 0.60) + (0.07 × 0.40)] × 100 = 10
Calculation of Overall Cost of Capital
Here optimal capital structure is one, with 90 per cent equity and 10 per cent debt since K is less
(9.6).
8.5 Determinants of Capital Structure
Capital structure may be determined at the time of promotion of the firm or during the latter
stages. But determining optimal capital structure at the time of promotion is very important and
it should be designed very carefully. Management of any firm should set a target capital structure
and the subsequent financing decisions should be made with a view to achieve the target capital
structure. Construction of capital structure, is difficult, since it involves a complex trade off
among several factors or considerations. Keeping the objective of wealth maximisation in mind,
capital structure has to be determined. The following factors affect optimal capital structure:
1. Tax benefit of Debt: Debt is the cheapest source of long-term finance, when compared with
other source equity, because the interest on debt finance is a tax-deductible expense.
Hence, debt can be accepted as a tax-sheltered source of finance, which helps in shareholder
wealth maximisation.
2. Flexibility: Flexibility is one of the most important and serious factors, which is considered
in determining capital structure. Flexibility is the firm’s ability to adopt its capital structure
to the needs of changing conditions. Changing conditions may be, need of more funds for
investments or having substantial funds that are already raised. Whenever there is a need
to have more funds to finance profitable investments, the firm should be able to rise
without delay and less cost. On the other hand, whenever there are surplus funds, the firm
should be able to repay them. The above two conditions are fulfilled only when there is a
flexible capital structure. In other words, the financial plan of a firm should be able to
change according to their operating strategy and needs. The flexibility of capital structure
depends on the flexibility in fixed charges, the covenants and debt capacity of the firm.
3. Control: The equity shareholder have voting right to elect the directors of the company.
Raising funds by way of issue of new equity shares to the public may lead to loss of
control. If the management wants to have total control on the firm then, it may require to
raise funds through non-voting right instrument that is debt source of finance. But the
firm needs to pay interest compulsory on debt finance. Debt finance is preferred only
when the firm’s debt service capacity is good. Otherwise the creditors may seize the assets
of the firm to satisfy their claims (interest). In this situation management would lose all
control. It might be better to sacrifice a measure of control by some additional equity
finance rather than run the risk of loosing all control to creditors by employing too much
debt. Widely held companies can raise funds by way of issue of equity shares, since the
shares are widely scattered and majority of shareholder are interested in the return. At the
same time if they are not satisfied with the firm, they will switch over to some other firm,
where they expect higher return.
178 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY