Page 30 - DMGT207_MANAGEMENT_OF_FINANCES
P. 30
Unit 2: Time Value of Money
EAR for 10% compounded quarterly Notes
0.10 4
EAR 1 1 0.1038 10.38%
4
Thus, we see that 10% compounded quarterly is actually a higher interest rate than 10.1%
compounded semiannually. Given a choice, we would prefer to invest at 10% compounded
quarterly.
Annuity Due
An annuity-due is an annuity whose payments are made at the beginning of each period. Some
of the common examples of annuity due are deposits in savings, rent or lease payments, and
insurance premiums.
Because each annuity payment is allowed to compound for one extra period, the value of an
annuity-due is equal to the value of the corresponding ordinary annuity multiplied by (1+i).
Present value of Annuity Due
PVA = CIF (FVIF ) (1 + I) or
n I . n
1 1 I n
PVA CIF 1 I
n
I
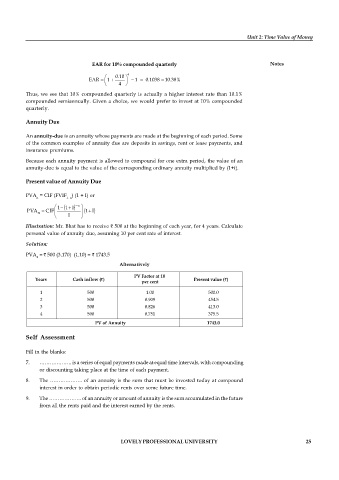
Illustration: Mr. Bhat has to receive 500 at the beginning of each year, for 4 years. Calculate
personal value of annuity due, assuming 10 per cent rate of interest.
Solution:
PVA = 500 (3.170) (1.10) = 1743.5
4
Alternatively
PV Factor at 10
Years Cash inflow ( ) Present value ( )
per cent
1 500 1.00 500.0
2 500 0.909 454.5
3 500 0.826 413.0
4 500 0.751 375.5
PV of Annuity 1743.0
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
7. ………………. is a series of equal payments made at equal time intervals, with compounding
or discounting taking place at the time of each payment.
8. The ………………. of an annuity is the sum that must be invested today at compound
interest in order to obtain periodic rents over some future time.
9. The ………………. of an annuity or amount of annuity is the sum accumulated in the future
from all the rents paid and the interest earned by the rents.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 25