Page 126 - DSOC201_SOCIAL_STRUCTURE_AND_SOCIAL_CHANGE_ENGLISH
P. 126
Unit 5: Kinship
Murdock (1949: 97-100) has classified kinship terms on three bases: Notes
1. Mode of Use of Kinship Terms
This refers to the kinship term employed either in direct address (called term of address) or in
indirect reference (called term of reference). Some people have distinct set of terms for address
and reference, for example, pita (term of reference) and baba (term of address) for father, or mata
and amba for mother, but others make only grammatical distinctions or none at all. Terms of
address tend to reveal more duplication and over-lapping; for example just as in English language
the term ‘uncle’ is used for a number of people (like FaFa, MoBr, father’s elderly cousin, and for
all elderly persons); similarly in Indian languages, the term bhai is used not only for one’s own
brother but also for cousin and many other persons.
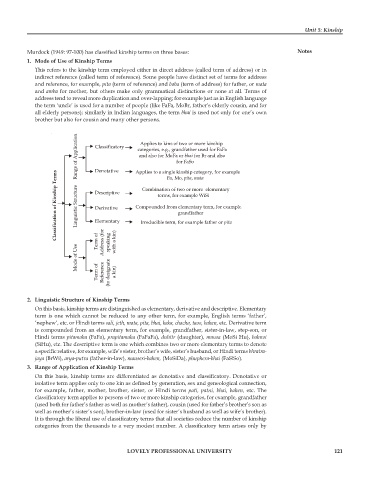
Range of Application Classificatory Applies to a single kinship category, for example
Applies to kins of two or more kinship
categories, e.g., grandfather used for FaFa
and also for MoFa or bhai
for Br and also
for FaSo
Denotative
Classification of Kinship Terms Linguistic Structure Descriptive Irreducible term, for example father or pita
, mata
Fa, Mo, pita
Combination of two or more elementary
terms, for example WiSi
Compounded from elementary term, for example
Derivative
grandfather
Elementary
Mode of Use Term of Address (for speaking with a kin)
Term of Reference (to designate a kin)
2. Linguistic Structure of Kinship Terms
On this basis, kinship terms are distinguished as elementary, derivative and descriptive. Elementary
term is one which cannot be reduced to any other term, for example, English terms ‘father’,
‘nephew’, etc. or Hindi terms sali, jeth, mata, pita, bhai, kaka, chacha, taoo, bahen, etc. Derivative term
is compounded from an elementary term, for example, grandfather, sister-in-law, step-son, or
Hindi terms pitamaha (FaFa), prapitamaha (FaFaFa), duhitr (daughter), mausa (MoSi Hu), bahnoi
(SiHu), etc. The descriptive term is one which combines two or more elementary terms to denote
a specific relative, for example, wife’s sister, brother’s wife, sister’s husband, or Hindi terms bhratra-
jaya (BrWi), arya-putra (father-in-law), mauseri-bahen, (MoSiDa), phuphera-bhai (FaSiSo).
3. Range of Application of Kinship Terms
On this basis, kinship terms are differentiated as denotative and classificatory. Denotative or
isolative term applies only to one kin as defined by generation, sex and geneological connection,
for example, father, mother, brother, sister, or Hindi terms pati, patni, bhai, bahen, etc. The
classificatory term applies to persons of two or more kinship categories, for example, grandfather
(used both for father’s father as well as mother’s father), cousin (used for father’s brother’s son as
well as mother’s sister’s son), brother-in-law (used for sister’s husband as well as wife’s brother).
It is through the liberal use of classificatory terms that all societies reduce the number of kinship
categories from the thousands to a very modest number. A classificatory term arises only by
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 121