Page 157 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 157
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes There are four important properties of transactions that a DBMS must ensure to maintain data in
the face of concurrent access and system failures:
1. Users should be able to regard the execution of each transaction as atomic: either all
actions are carried out or none are. Users should not have to worry about the effect of
incomplete transactions (say, when a system crash occurs).
2. Each transaction, run by itself with no concurrent execution of other transactions, must
preserve the consistency of the database. This property is called consistency, and the
DBMS assumes that it holds for each transaction. Ensuring this property of a transaction is
the responsibility of the user.
3. Users should be able to understand a transaction without considering the effect of other
concurrently executing transactions, even if the DBMS interleaves the actions of several
transactions for performance reasons. This property is sometimes referred to as isolation:
Transactions are isolated, or protected, from the effects of concurrently scheduling other
transactions.
4. Once the DBMS informs the user that a transaction has been successfully completed, its
effects should persist even if the system crashes before all its changes are reflected on disk.
This property is called durability.
9.2 Transaction State
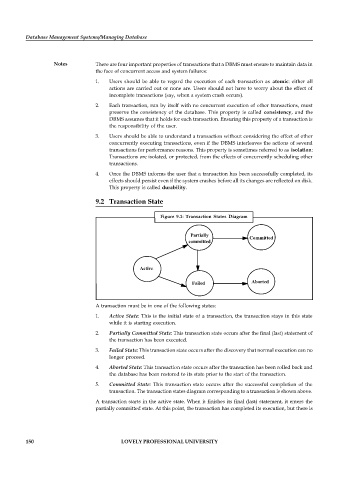
Figure 9.1: Transaction States Diagram
Partially
Committed
committed
Active
Failed Aborted
A transaction must be in one of the following states:
1. Active State: This is the initial state of a transaction, the transaction stays in this state
while it is starting execution.
2. Partially Committed State: This transaction state occurs after the final (last) statement of
the transaction has been executed.
3. Failed State: This transaction state occurs after the discovery that normal execution can no
longer proceed.
4. Aborted State: This transaction state occurs after the transaction has been rolled back and
the database has been restored to its state prior to the start of the transaction.
5. Committed State: This transaction state occurs after the successful completion of the
transaction. The transaction states diagram corresponding to a transaction is shown above.
A transaction starts in the active state. When it finishes its final (last) statement, it enters the
partially committed state. At this point, the transaction has completed its execution, but there is
150 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY