Page 25 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 25
Database Management Systems/Managing Database
Notes Concepts
SQL uses concepts “table”, “column”, “row” instead of “relvar”, “attribute”, “tuple”. These are
not merely differences in terminology.
Example: A “table” may contain duplicate rows, whereas the same tuple cannot appear
more than once in a relation.
Database
An idealized, very simple example of a description of some relvars and their attributes:
1. Customer (Customer ID, Tax ID, Name, Address, City, State, Zip, Phone)
2. Order (Order No, Customer ID, Invoice No, Date Placed, Date Promised, Terms, Status)
3. Order Line (Order No, Order Line No, Product Code, Qty)
4. Invoice (Invoice No, Customer ID, Order No, Date, Status)
5. Invoice Line (Invoice No, Line No, Product Code, Qty Shipped)
6. Product (Product Code, Product Description)
In this design we have six relvars: Customer, Order, Order Line, Invoice, Invoice Line and
Product. The bold, underlined attributes are candidate keys. The non-bold, underlined attributes
are foreign keys.
Usually one candidate key is arbitrarily chosen to be called the primary key and used in preference
over the other candidate keys, which are then called alternate keys.
A candidate key is a unique identifier enforcing that no tuple will be duplicated; this would
make the relation into something else, namely a bag, by violating the basic definition of a set.
Both foreign keys and superkeys (which includes candidate keys) can be composite, that is, can
be composed of several attributes. Below is a tabular depiction of a relation of our example
Customer relvar; a relation can be thought of as a value that can be attributed to a relvar.
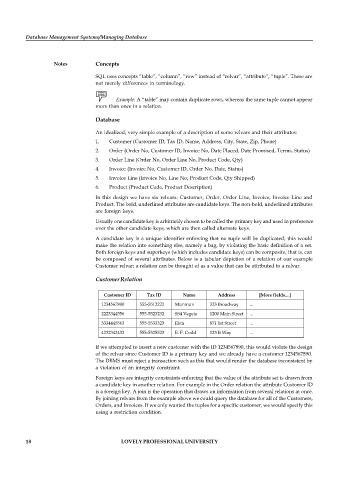
Customer Relation
Customer ID Tax ID Name Address [More fields....]
1234567890 555-5512222 Munmun 323 Broadway ...
2223344556 555-5523232 SS4 Vegeta 1200 Main Street ...
3334445563 555-5533323 Ekta 871 1st Street ...
4232342432 555-5325523 E. F. Codd 123 It Way ...
If we attempted to insert a new customer with the ID 1234567890, this would violate the design
of the relvar since Customer ID is a primary key and we already have a customer 1234567890.
The DBMS must reject a transaction such as this that would render the database inconsistent by
a violation of an integrity constraint.
Foreign keys are integrity constraints enforcing that the value of the attribute set is drawn from
a candidate key in another relation. For example in the Order relation the attribute Customer ID
is a foreign key. A join is the operation that draws on information from several relations at once.
By joining relvars from the example above we could query the database for all of the Customers,
Orders, and Invoices. If we only wanted the tuples for a specific customer, we would specify this
using a restriction condition.
18 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY