Page 34 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 34
Unit 2: Database Relational Model
of union operator is that both the relations must be union-compatible, i.e., both the relations Notes
must have the same number of columns and also these columns must have the same domain
(type of data being stored in each column).
If A and B are two relations and are union compatible then union of these two relations is
expressed as:
A B A B returns uniquely all the tuples of A and B.
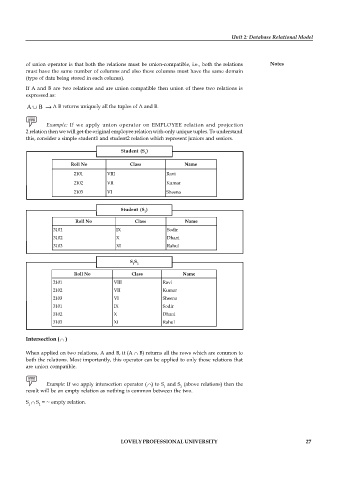
Example: If we apply union operator on EMPLOYEE relation and projection
2 relation then we will get the original employee relation with-only unique tuples. To understand
this, consider a simple student1 and student2 relation which represent juniors and seniors.
Student (S )
1
Roll No Class Name
2101 VIII Ravi
2102 VII Kumar
2103 VI Sheena
Student (S )
2
Roll No Class Name
3101 IX Sodir
3102 X Dhani
3103 XI Rahul
S S
1 2
Roll No Class Name
2101 VIII Ravi
2102 VII Kumar
2103 VI Sheena
3101 IX Sodir
3102 X Dhani
3103 XI Rahul
Intersection ( )
When applied on two relations, A and B, it (A B) returns all the rows which are common to
both the relations. Most importantly, this operator can be applied to only those relations that
are union compatible.
Example: If we apply intersection operator ( ) to S and S (above relations) then the
1 2
result will be an empty relation as nothing is common between the two.
S S = ~ empty relation.
1 2
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 27