Page 82 - DCAP402_DCAO204_DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM_MANAGING DATABASE
P. 82
Unit 5: Integrity Constraints
UNIQUE as a Table Constraint: Notes
CREATE TABLE client master
(client_no varchar2(6), name varchar2(20),
addressl varchar2(30), address2 varchar2(30),
city varchar2(15), state varchar2(15), pincode number(6),
remarks varchar2(60), bal_due number(lO,2),
CONSTRAINT cnmn_ukey UNIQUE (client_no));
Default Value Concepts
At the time of cell creation a ‘default value’ can be assigned to it. When the user is loading a
‘record’ with values and leaves this cell empty, the DBA will automatically load this cell with the
default value specified – The data type of the default value should match the data type of the
column. You can use the default clause to specify any default value you want.
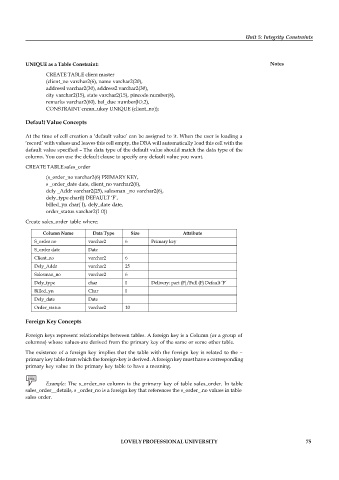
CREATE TABLE sales_order
(s_order_no varchar2(6) PRIMARY KEY,
s _order_date date, client_no varchar2(6),
dely _Addr varchar2(25), salesman _no varchar2(6),
dely_type char(l) DEFAULT ‘F’,
billed_yn char( l), dely_date date,
order_status varchar2(1 0))
Create sales_order table where:
Column Name Data Type Size Attribute
S_order no varchar2 6 Primary key
S_order date Date
Client_no varchar2 6
Dely_Addr varchar2 25
Salesman_no varchar2 6
Dely_type char I Delivery: part (P)/Full (F) Default ‘F’
Billed_yn Char I
Dely_date Date
Order_status varchar2 10
Foreign Key Concepts
Foreign keys represent relationships between tables. A foreign key is a Column (or a group of
columns) whose values-are derived from the primary key of the same or some other table.
The existence of a foreign key implies that the table with the foreign key is related to the –
primary key table from which the foreign-key is derived. A foreign key must have a corresponding
primary key value in the primary key table to have a meaning.
Example: The s_order_no column is the primary key of table sales_order. In table
sales_order__details, s _order_no is a foreign key that references the s_order_.no values in table
sales order.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75