Page 128 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 128
Unit 8: Data Link Protocols
8.7 Ethernet Technologies Notes
Among LAN standards, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet has become one of the most used LAN media. Its
ample use and wide availability has made it one of the cheapest LAN media. Moreover, it can
carry high-speed transmission. The evolution of Ethernet to such a widely accepted media may
be traced back to late 1970s when the first Ethernet standard was created by Xerox. Around 1984,
DIX (a consortium of Digital, Intel, and Xerox) and IEEE created standards for Ethernet which are
popularly known as the IEEE 802.1. Subsequently, these groups segregated their work and
worked as the Logical Link Control (LLC) Group focussing on end-to-end connectivity and
came to be called the IEEE 802.2 Committee. Another group, called the Data Link and Medium
Access Control (DLMAC) took the responsibility for developing medium access protocols. This
group later formed committees for Ethernet (802.3), Token Bus (802.4), and Token Ring (802.5).
Ethernet is the least expensive high-speed LAN alternative. It transmits and receives data at a
speed of 10 million bits per second. Data is transferred between wiring closets using either a
heavy coaxial cable (thick net) or fibre optic cable. Thick net coaxial is still used for medium-
long distances where medium levels of reliability are needed. Fibre goes a further distance and
has greater reliability but a higher cost. To connect a number of workstations within the same
room, a light duty coaxial cable called thin net is commonly used. These other media reflect an
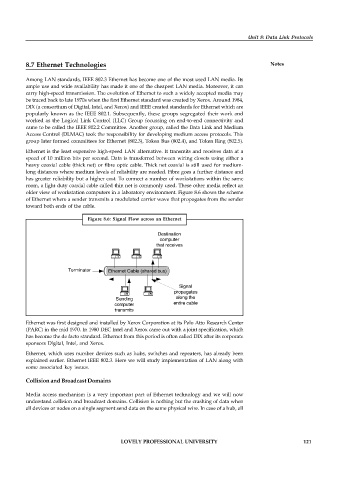
older view of workstation computers in a laboratory environment. Figure 8.6 shows the scheme
of Ethernet where a sender transmits a modulated carrier wave that propagates from the sender
toward both ends of the cable.
Figure 8.6: Signal Flow across an Ethernet
Destination
computer
that receives
Terminator Ethernet Cable (shared bus)
Signal
propagates
Sending along the
computer entire cable
transmits
Ethernet was first designed and installed by Xerox Corporation at its Palo Atto Research Center
(PARC) in the mid 1970. In 1980 DEC Intel and Xerox came out with a joint specification, which
has become the de facto standard. Ethernet from this period is often called DIX after its corporate
sponsors Digital, Intel, and Xerox.
Ethernet, which uses number devices such as hubs, switches and repeaters, has already been
explained earlier. Ethernet IEEE 802.3. Here we will study implementation of LAN along with
some associated key issues.
Collision and Broadcast Domains
Media access mechanism is a very important part of Ethernet technology and we will now
understand collision and broadcast domains. Collision is nothing but the crashing of data when
all devices or nodes on a single segment send data on the same physical wire. In case of a hub, all
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 121