Page 157 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 157
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes
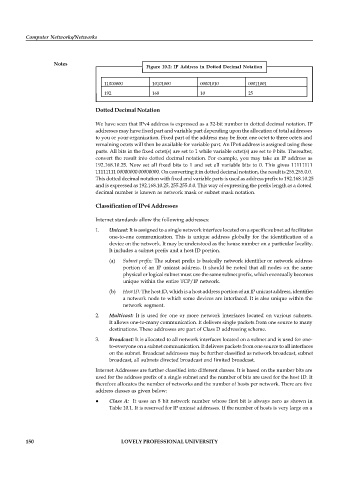
Figure 10.2: IP Address in Dotted Decimal Notation
11000000 10101000 00001010 00011001
192 168 10 25
Dotted Decimal Notation
We have seen that IPv4 address is expressed as a 32-bit number in dotted decimal notation. IP
addresses may have fixed part and variable part depending upon the allocation of total addresses
to you or your organization. Fixed part of the address may be from one octet to three octets and
remaining octets will then be available for variable part. An IPv4 address is assigned using these
parts. All bits in the fixed octet(s) are set to 1 while variable octet(s) are set to 0 bits. Thereafter,
convert the result into dotted decimal notation. For example, you may take an IP address as
192.168.10.25. Now set all fixed bits to 1 and set all variable bits to 0. This gives 11111111
11111111 00000000 00000000. On converting it in dotted decimal notation, the result is 255.255.0.0.
This dotted decimal notation with fixed and variable parts is used as address prefix to 192.168.10.25
and is expressed as 192.168.10.25, 255.255.0.0. This way of expressing the prefix length as a dotted
decimal number is known as network mask or subnet mask notation.
Classification of IPv4 Addresses
Internet standards allow the following addresses:
1. Unicast: It is assigned to a single network interface located on a specific subnet ad facilitates
one-to-one communication. This is unique address globally for the identification of a
device on the network. It may be understood as the house number on a particular locality.
It includes a subnet prefix and a host ID portion.
(a) Subnet prefix: The subnet prefix is basically network identifier or network address
portion of an IP unicast address. It should be noted that all nodes on the same
physical or logical subnet must use the same subnet prefix, which eventually becomes
unique within the entire TCP/IP network.
(b) Host ID: The host ID, which is a host address portion of an IP unicast address, identifies
a network node to which some devices are interfaced. It is also unique within the
network segment.
2. Multicast: It is used for one or more network interfaces located on various subnets.
It allows one-to-many communication. It delivers single packets from one source to many
destinations. These addresses are part of Class D addressing scheme.
3. Broadcast: It is allocated to all network interfaces located on a subnet and is used for one-
to-everyone on a subnet communication. It delivers packets from one source to all interfaces
on the subnet. Broadcast addresses may be further classified as network broadcast, subnet
broadcast, all subnets directed broadcast and limited broadcast.
Internet Addresses are further classified into different classes. It is based on the number bits are
used for the address prefix of a single subnet and the number of bits are used for the host ID. It
therefore allocates the number of networks and the number of hosts per network. There are five
address classes as given below:
Class A: It uses an 8 bit network number whose first bit is always zero as shown in
Table 10.1. It is reserved for IP unicast addresses. If the number of hosts is very large on a
150 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY