Page 163 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 163
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes 10.2.3 Congestion Prevention Policies
Open loop systems are designed to minimize the congestion at the place of its origin. Applying
congestion prevention policies at different layers solves the problem in case of open loop
systems. The policies at data link, network and transport layers that affects congestion is given
below:
Data link layer: The issues such as retransmission of packets, out of order caching,
acknowledgement of the received packets from destination machine and flow control affect
congestion at this layer.
Network layer: Setting up of virtual channel and datagram inside the subnet, packet queueing
and forwarding at router, dropping of packets at router, routing algorithms, packet lifetime
management, etc are the factors affecting congestion at this layer.
Transport layer: Retransmission of packets, out of order caching, acknowledgement of the
received packets from destination machine, flow control mechanism, time out packets, etc.
affect congestion at this layer.
Traffic Shaping
One of the main reasons for congestion is the bursty traffic. Another cause is the transmission of
packets at an unpredictable rate. Hence, the traffic shaping approach includes transmission of
packets at uniform rate and in more predictable rate in case of open loop method. Thus, the
traffic shaping attempts to regularize the average rate of data transmission. For example, the
ATM networks exploit this method to a greater extent. To reduce congestion, the user and the
subnet agree on a certain traffic pattern in a virtual circuit. Such agreements are of great importance
for transfer of real time audio and video connections, which do not tolerate congestion.
Monitoring traffic pattern is called traffic policing.
Leaky Bucket
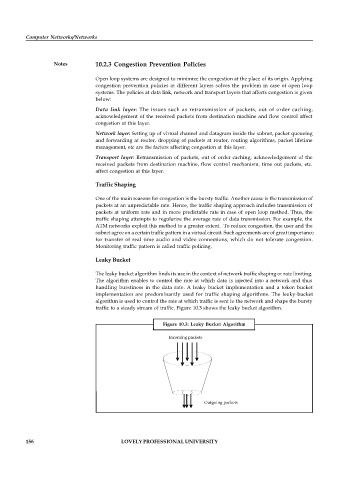
The leaky bucket algorithm finds its use in the context of network traffic shaping or rate limiting.
The algorithm enables to control the rate at which data is injected into a network and thus
handling burstiness in the data rate. A leaky bucket implementation and a token bucket
implementation are predominantly used for traffic shaping algorithms. The leaky-bucket
algorithm is used to control the rate at which traffic is sent to the network and shape the bursty
traffic to a steady stream of traffic. Figure 10.3 shows the leaky bucket algorithm.
Figure 10.3: Leaky Bucket Algorithm
Incoming packets
Outgoing packets
156 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY