Page 79 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 79
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes
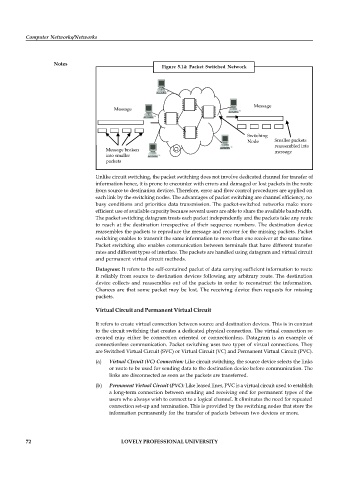
Figure 5.14: Packet Switched Network
Message
Message
Switching
Node Smaller packets
reassembled into
Message broken message
into smaller
packets
Figure 10.5 Packet switched network
Unlike circuit switching, the packet switching does not involve dedicated channel for transfer of
information hence, it is prone to encounter with errors and damaged or lost packets in the route
from source to destination devices. Therefore, error and flow control procedures are applied on
each link by the switching nodes. The advantages of packet switching are channel efficiency, no
busy conditions and priorities data transmission. The packet-switched networks make more
efficient use of available capacity because several users are able to share the available bandwidth.
The packet switching datagram treats each packet independently and the packets take any route
to reach at the destination irrespective of their sequence numbers. The destination device
reassembles the packets to reproduce the message and recover for the missing packets. Packet
switching enables to transmit the same information to more than one receiver at the same time.
Packet switching also enables communication between terminals that have different transfer
rates and different types of interface. The packets are handled using datagram and virtual circuit
and permanent virtual circuit methods.
Datagram: It refers to the self-contained packet of data carrying sufficient information to route
it reliably from source to destination devices following any arbitrary route. The destination
device collects and reassembles out of the packets in order to reconstruct the information.
Chances are that some packet may be lost. The receiving device then requests for missing
packets.
Virtual Circuit and Permanent Virtual Circuit
It refers to create virtual connection between source and destination devices. This is in contrast
to the circuit switching that creates a dedicated physical connection. The virtual connection so
created may either be connection oriented or connectionless. Datagram is an example of
connectionless communication. Packet switching uses two types of virtual connections. They
are Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC) or Virtual Circuit (VC) and Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC).
(a) Virtual CIrcuit (VC) Connection: Like circuit switching, the source device selects the links
or route to be used for sending data to the destination device before communication. The
links are disconnected as soon as the packets are transferred.
(b) Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC): Like leased lines, PVC is a virtual circuit used to establish
a long-term connection between sending and receiving end for permanent types of the
users who always wish to connect to a logical channel. It eliminates the need for repeated
connection set-up and termination. This is provided by the switching nodes that store the
information permanently for the transfer of packets between two devices or more.
72 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY