Page 85 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 85
Computer Networks/Networks
Notes
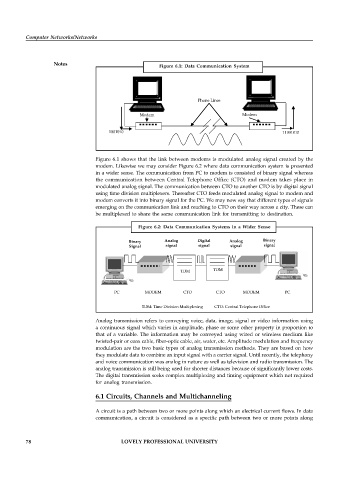
Figure 6.1: Data Communication System
Phone Lines
Modem Modem
11001010 11001010
Figure 6.1 shows that the link between modems is modulated analog signal created by the
modem. Likewise we may consider Figure 6.2 where data communication system is presented
in a wider sense. The communication from PC to modem is consisted of binary signal whereas
the communication between Central Telephone Office (CTO) and modem takes place in
modulated analog signal. The communication between CTO to another CTO is by digital signal
using time division multiplexers. Thereafter CTO feeds modulated analog signal to modem and
modem converts it into binary signal for the PC. We may now say that different types of signals
emerging on the communication link and reaching to CTO on their way across a city. These can
be multiplexed to share the same communication link for transmitting to destination.
Figure 6.2: Data Communication Systems in a Wider Sense
Binary Analog Digital Analog Binary
Signal signal signal signal signal
TDM
TDM
PC MODEM CTO CTO MODEM PC
TDM: Time Division Multiplexing CTO: Central Telephone Office
Analog transmission refers to conveying voice, data, image, signal or video information using
a continuous signal which varies in amplitude, phase or some other property in proportion to
that of a variable. The information may be conveyed using wired or wireless medium like
twisted-pair or coax cable, fiber-optic cable, air, water, etc. Amplitude modulation and frequency
modulation are the two basic types of analog transmission methods. They are based on how
they modulate data to combine an input signal with a carrier signal. Until recently, the telephony
and voice communication was analog in nature as well as television and radio transmission. The
analog transmission is still being used for shorter distances because of significantly lower costs.
The digital transmission seeks complex multiplexing and timing equipment which not required
for analog transmission.
6.1 Circuits, Channels and Multichanneling
A circuit is a path between two or more points along which an electrical current flows. In data
communication, a circuit is considered as a specific path between two or more points along
78 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY