Page 92 - DCAP207_NETWORKS_DCAP406_COMPUTER_NETWORKS
P. 92
Unit 6: Multiplexing
signal are that it provides efficient transmission between sending device and receiving device Notes
and needs smaller sizes of antenna because of higher frequency of transmission.
6.4.1 Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
ASK describes the technique how the carrier wave is multiplied by the digital signal f (t) so that
the strength of the carrier wave is varied to represent binary 0 and 1. In ASK, both the frequency
and phase of an analog waveform are kept uniform while amplitude is changed in accordance
with the digital signal.
Notes Mathematically, the modulated carrier signal y(t) is:
y(t) = f(t) × sin(2pfct + j) where fc is a carrier frequency and t is instantaneous time.
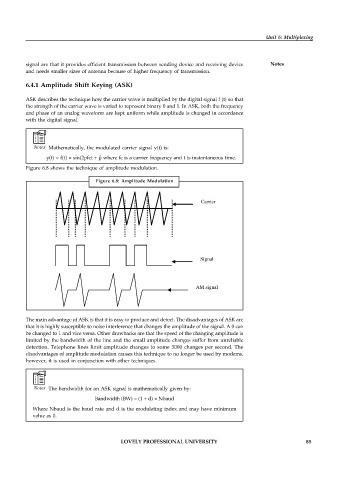
Figure 6.8 shows the technique of amplitude modulation.
Figure 6.8: Amplitude Modulation
Carrier
Signal
AM signal
The main advantage of ASK is that it is easy to produce and detect. The disadvantages of ASK are
that it is highly susceptible to noise interference that changes the amplitude of the signal. A 0 can
be changed to 1 and vice versa. Other drawbacks are that the speed of the changing amplitude is
limited by the bandwidth of the line and the small amplitude changes suffer from unreliable
detection. Telephone lines limit amplitude changes to some 3000 changes per second. The
disadvantages of amplitude modulation causes this technique to no longer be used by modems,
however, it is used in conjunction with other techniques.
Notes The bandwidth for an ASK signal is mathematically given by:
Bandwidth (BW) = (1 + d) × Nbaud
Where Nbaud is the baud rate and d is the modulating index and may have minimum
value as 0.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 85