Page 36 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 36
Unit 2: Strategy and Operations Strategy
back and forth among the generic strategies. In addition, the organization would be amenable Notes
to a blurring of the corporate culture and conflicting motivation system. Obviously, this happens
when organizations do not exercise their options based on their capabilities and limitations.
An organization must take a fundamental strategic decision to select one of the three generic
strategies. Failing to develop a strategy in any of the three directions will result in low profitability.
It will either lose the high volume customers who demand low prices or operate with reduced
profits to lure this business away from the low cost competition. It will also lose high margin
businesses to competition that have achieved differentiation overall.
This seems to indicate that in many industries there is a U-shaped relationship between
profitability and market share. The profitability is high with low market share using a
differentiation strategy and a high market share using a cost leader strategy.
Example: In the automobile industry the profit leaders are General Motors that has a
price leadership strategy and Mercedes, which has a differentiation strategy.
The three strategies are based on competing differently in the marketplace. They construct
different types of defences against competitive forces. The types of risks they face are also
different. However, there are two types of risks that are common to all of them:
1. Failing to attain or sustain the strategy, and
2. Erosion in the value of the strategic advantage with industry evolution.
Cost leadership imposes a severe burden on the organization to keep up its position. It means
the organization has to reinvest in modern equipment so as to keep reaping all the economies
of scale. In addition, it must keep honing its process engineering core capability. Similarly,
differentiation requires investments in a strong R&D on a continuous basis and the ability to
attract the right type of people into the company. A summary of the risks for the different
strategic options is given in Table below:
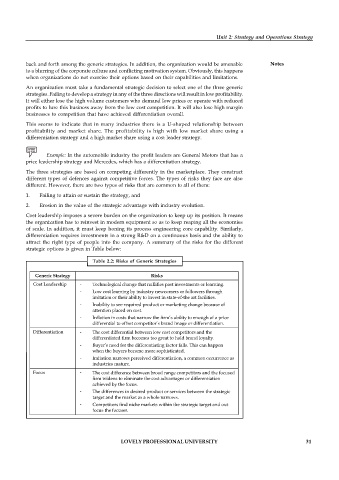
Table 2.2: Risks of Generic Strategies
Generic Strategy Risks
Cost Leadership - Technological change that nullifies past investments or learning.
- Low cost learning by industry newcomers or followers through
imitation or their ability to invest in state-of-the art facilities.
- Inability to see required product or marketing change because of
attention placed on cost.
- Inflation in costs that narrow the firm’s ability to enough of a price
differential to offset competitor’s brand image or differentiation.
Differentiation - The cost differential between low cost competitors and the
differentiated firm becomes too great to hold brand loyalty.
- Buyer’s need for the differentiating factor falls. This can happen
when the buyers become more sophisticated.
- Imitation narrows perceived differentiation, a common occurrence as
industries mature.
Focus - The cost difference between broad range competitors and the focused
firm widens to eliminate the cost advantages or differentiation
achieved by the focus.
- The differences in desired product or services between the strategic
target and the market as a whole narrows.
- Competitors find niche markets within the strategic target and out
focus the focuser.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 31