Page 175 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 175
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
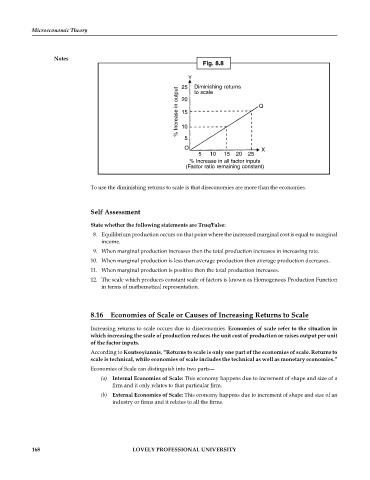
Fig. 8.8
Y Diminishing returns
25
% Increase in output 20 Q
to scale
15
10
5
O X
5 10 15 20 25
% Increase in all factor inputs
(Factor ratio remaining constant)
To use the diminishing returns to scale is that diseconomies are more than the economies.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are True/False:
8. Equilibrium production occurs on that point where the increased marginal cost is equal to marginal
income.
9. When marginal production increases then the total production increases in increasing rate.
10. When marginal production is less than average production then average production decreases.
11. When marginal production is positive then the total production increases.
12. The scale which produces constant scale of factors is known as Homogenous Production Function
in terms of mathematical representation.
8.16 Economies of Scale or Causes of Increasing Returns to Scale
Increasing returns to scale occurs due to diseconomies. Economies of scale refer to the situation in
which increasing the scale of production reduces the unit cost of production or raises output per unit
of the factor inputs.
According to Koutsoyiannis, “Returns to scale is only one part of the economies of scale. Returns to
scale is technical, while economies of scale includes the technical as well as monetary economies.”
Economies of Scale can distinguish into two parts—
(a) Internal Economies of Scale: This economy happens due to increment of shape and size of a
firm and it only relates to that particular firm.
(b) External Economies of Scale: This economy happens due to increment of shape and size of an
industry or firms and it relates to all the firms.
168 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY