Page 210 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 210
Unit-10: Isoquant Curve
, b
Notes
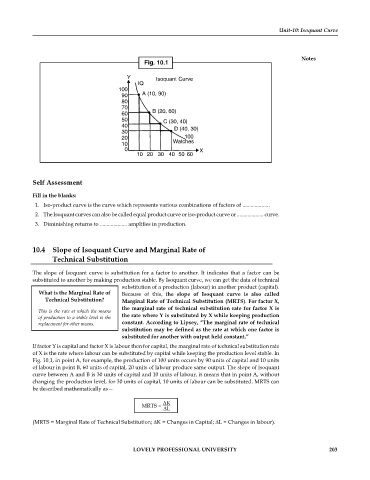
Fig. 10.1
Y Isoquant Curve
IQ
100
90 A (10, 90)
80
70
60 B (20, 60)
50 C (30, 40)
40 D (40, 30)
30
20 100
10 Watches
0 X
10 20 30 40 50 60
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Iso-product curve is the curve which represents various combinations of factors of ....................
2. The Isoquant curves can also be called equal product curve or iso-product curve or .................... curve.
3. Diminishing returns to .................... amplifies in production.
10.4 Slope of Isoquant Curve and Marginal Rate of
Technical Substitution
The slope of Isoquant curve is substitution for a factor to another. It indicates that a factor can be
substituted to another by making production stable. By Isoquant curve, we can get the data of technical
substitution of a production (labour) in another product (capital).
What is the Marginal Rate of Because of this, the slope of Isoquant curve is also called
Technical Substitution? Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution (MRTS). For factor X,
the marginal rate of technical substitution rate for factor X is
This is the rate at which the means
of production to a stable level is the the rate where Y is substituted by X while keeping production
replacement for other means. constant. According to Lipsey, “The marginal rate of technical
substitution may be defined as the rate at which one factor is
substituted for another with output held constant.”
If factor Y is capital and factor X is labour then for capital, the marginal rate of technical substitution rate
of X is the rate where labour can be substituted by capital while keeping the production level stable. In
Fig. 10.1, in point A, for example, the production of 100 units occurs by 90 units of capital and 10 units
of labour in point B, 60 units of capital, 20 units of labour produce same output. The slope of Isoquant
curve between A and B is 30 units of capital and 10 units of labour, it means that in point A, without
changing the production level, for 30 units of capital, 10 units of labour can be substituted. MRTS can
be described mathematically as—
∆K
MRTS = ___
∆L
(MRTS = Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution; ∆K = Changes in Capital; ∆L = Changes in labour).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 203