Page 343 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 343
Microeconomic Theory
Notes Then with CC curve, in one of the directions, production of a firm can be caused for the increment of
the cost of the other firm. So, the condition indicates that any factor used for any function that will be
efficient.
Self Assessment
Multiple choice questions:
5. Hicks has fixed to know the optimum of pareto ........................ .
(a) maximum condition (b) monies (c) arts (d) none of these
6. The factor of production is totally ........................ .
(a) active (b) motion (c) efficient (d) none of these
7. Each objects has .........................
(a) divisible (b) remainder (c) non-divisible (d) none of these
8. Each production unit with others is .........................
(a) not free (b) constant (c) free (d) none of these
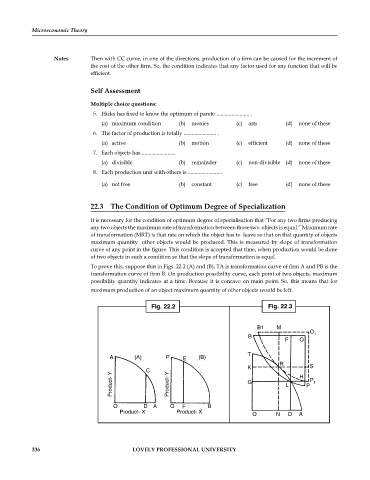
22.3 The Condition of Optimum Degree of Specialization
It is necessary for the condition of optimum degree of specialisation that “For any two firms producing
any two objects the maximum rate of transformation between those two objects is equal.” Maximum rate
of transformation (MRT) is that rate on which the object has to leave so that on that quantity of objects
maximum quantity other objects would be produced. This is measured by slope of transformation
curve of any point in the figure. This condition is accepted that time, when production would be done
of two objects in such a condition so that the slope of transformation is equal.
To prove this, suppose that in Figs. 22.2 (A) and (B), TA is transformation curve of firm A and PB is the
transformation curve of firm B. On production possibility curve, each point of two objects, maximum
possibility quantity indicates at a time. Because it is concave on main point. So, this means that for
maximum production of an object maximum quantity of other objects would be left.
Fig. 22.2 Fig. 22.3
B1 M
O 1
B
F O
T
A (A) P E (B)
R
K S
C H
Product- Y Product- Y G L P P 1
O D A O F B
Product- X Product- X
O N D A
336 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY