Page 351 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 351
Microeconomic Theory
Notes (i) Rivalrous or Rival Consumption
(ii) Non-rivalrous or Non-rival Consumption
(iii) Excludable
(iv) Non-excludable
(i) Rivalrous or Rival Consumption: The consumption of a production seems competitive when
the availability of this product gets low for person B if A consumes this. So both persons
(A and B) cannot use that product without fulfilling the satisfaction of each other. For example,
if Rahul drinks juice, Rohit cannot drink that juice; consumption by one person can exclude
others from consuming a product. So the products (like Apple, Pepsi, Cola, Machine etc.)
whose availability affects by consumption of others, is called Rivalrous product. This is
also called Private product.
(ii) Non-rivalrous or Non-rival Consumption: A product is non-rivalrous if a person (suppose A)
consume a product but product does not get out of market. Means the similar unit is available
for using more than one person.
Park, National Security, Roads, Bridges, etc. are non rivalrous products. A park, in which
everyone comes and goes and takes advantage to get relax. Thus, the persons of a nation can
use the security provided by national security system.
(iii) Excludable: A product is excludable when non payers cannot be differentiated from it. In other
words, when the law of property rights can use as only payers can use this facility. Ramesh eats
pizza but this is not available for Raju because Ramesh has ownership on this and he has only
ownership to eat pizza. Thus if you have bought a car, you are the owner of car and it is your
property right, so no other person can use this car without your permission. By an agreement
in property right, these types of products get excluded.
(iv) Non-excludable: These are the products for which no person can take rights. Roads, bridges,
street lights etc., are those products which cannot be separated to use by property rights because
these are the Common Property. Since the street lights are common property so it is difficult to
prevent non-payers to use this.
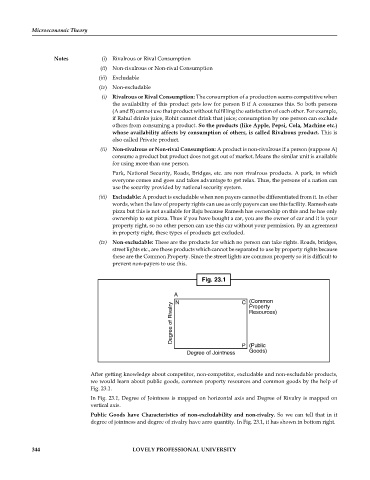
Fig. 23.1
A N C (Common
Degree of Rivalry Resources)
Property
P (Public
Goods)
Degree of Jointness
After getting knowledge about competitor, non-competitor, excludable and non-excludable products,
we would learn about public goods, common property resources and common goods by the help of
Fig. 23.1.
In Fig. 23.1, Degree of Jointness is mapped on horizontal axis and Degree of Rivalry is mapped on
vertical axis.
Public Goods have Characteristics of non-excludability and non-rivalry. So we can tell that in it
degree of jointness and degree of rivalry have zero quantity. In Fig. 23.1, it has shown in bottom right.
344 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY