Page 357 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 357
Microeconomic Theory
Notes 23.6 Negative Externality
When a person’s consumption or production process is affected to another person in society and he also
gets negative impact and he does not get any compensation, then it is called Negative Externalities. For
example, if a person established a steel factory near river and draws all pollutants in river. It clarifies
that due to this process the fishes get affected. Now the question is that is this effect, the owner of
steel factory would include this social cost (loss of fishing production) in his cost of steel production?
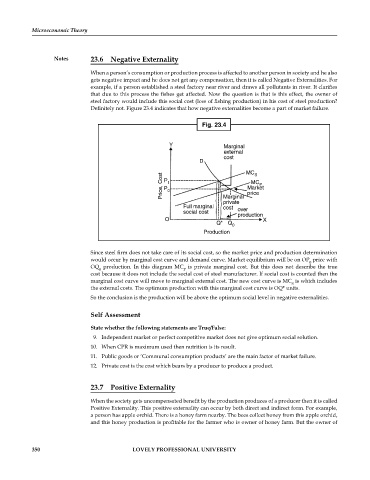
Definitely not. Figure 23.4 indicates that how negative externalities become a part of market failure.
Fig. 23.4
Y Marginal
external
cost
D
MC S
Price, Cost P 1 0 Market
MC
P
P
price
Marginal
private
Full marginal cost
social cost over
production
O X
Q* Q
0
Production
Since steel firm does not take care of its social cost, so the market price and production determination
would occur by marginal cost curve and demand curve. Market equilibrium will be on OP price with
0
OQ production. In this diagram MC is private marginal cost. But this does not describe the true
0
P
cost because it does not include the social cost of steel manufacturer. If social cost is counted then the
marginal cost curve will move to marginal external cost. The new cost curve is MC is which includes
S
the external costs. The optimum production with this marginal cost curve is OQ* units.
So the conclusion is the production will be above the optimum social level in negative externalities.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statements are True/False:
9. Independent market or perfect competitive market does not give optimum social solution.
10. When CPR is maximum used then nutrition is its result.
11. Public goods or ‘Communal consumption products’ are the main factor of market failure.
12. Private cost is the cost which bears by a producer to produce a product.
23.7 Positive Externality
When the society gets uncompensated benefit by the production produces of a producer then it is called
Positive Externality. This positive externality can occur by both direct and indirect form. For example,
a person has apple orchid. There is a honey farm nearby. The bees collect honey from this apple orchid,
and this honey production is profitable for the farmer who is owner of honey farm. But the owner of
350 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY