Page 46 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 46
Unit-3: Consumer Theory–Cardinal Utility Analysis
Notes
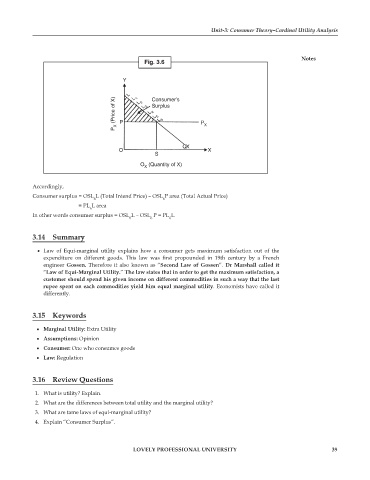
Fig. 3.6
Y
L L 1 L 2 Consumer’s
P X (Price of X) P L 3 L 4 Surplus P X
L 5
L 6
QX
O X
S
O (Quantity of X)
X
Accordingly,
Consumer surplus = OSL L (Total Intend Price) – OSL P area (Total Actual Price)
6 6
= PL L area
6
In other words consumer surplus = OSL L – OSL P = PL L
6 6 6
3.14 Summary
· Law of Equi-marginal utility explains how a consumer gets maximum satisfaction out of the
expenditure on different goods. This law was first propounded in 19th century by a French
engineer Gossen. Therefore it also known as “Second Law of Gossen”. Dr Marshall called it
“Law of Equi-Marginal Utility.” The law states that in order to get the maximum satisfaction, a
customer should spend his given income on different commodities in such a way that the last
rupee spent on each commodities yield him equal marginal utility. Economists have called it
differently.
3.15 Keywords
· Marginal Utility: Extra Utility
· Assumptions: Opinion
· Consumer: One who consumes goods
· Law: Regulation
3.16 Review Questions
1. What is utility? Explain.
2. What are the differences between total utility and the marginal utility?
3. What are tame laws of equi-marginal utility?
4. Explain “Consumer Surplus”.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 39