Page 100 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 100
Unit-11: The Theory of Acceleration
Operation of the Acceleration Principle Notes
Operation of the Acceleration Principle is explained by the help of example given in table.
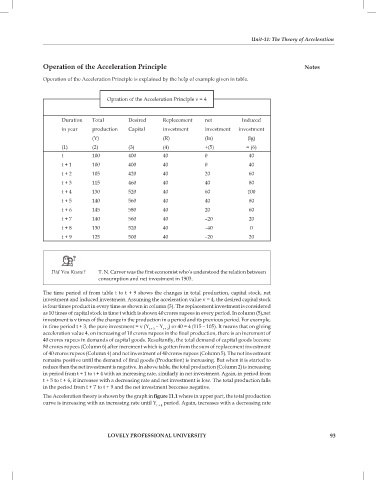
Opration of the Acceleration Principle n = 4
Duration Total Desired Replecement net Induced
in year production Capital investment investment investment
(Y) (R) (In) (lg)
(1) (2) (3) (4) +(5) = (6)
t 100 400 40 0 40
t + 1 100 400 40 0 40
t + 2 105 420 40 20 60
t + 3 115 460 40 40 80
t + 4 130 520 40 60 100
t + 5 140 560 40 40 80
t + 6 145 580 40 20 60
t + 7 140 560 40 –20 20
t + 8 130 520 40 –40 0
t + 9 125 500 40 –20 20
Did You Know? T. N. Carver was the first economist who’s understood the relation between
consumption and net investment in 1903.
The time period of from table t to t + 9 shows the changes in total production, capital stock, net
investment and induced investment. Assuming the acceleration value ν = 4, the desired capital stock
is four times product in every time as shown in column (3). The replacement investment is considered
as 10 times of capital stock in time t which is shown 40 crores rupees in every period. In column (5),net
investment is ν times of the change in the production in a period and its previous period. For example,
in time period t + 3, the pure investment = ν (Y t + 3 – Y t + 2 ) or 40 = 4 (115 – 105). It means that on giving
acceleration value 4, on increasing of 10 crores rupees in the final production, there is an increment of
40 crores rupees in demands of capital goods. Resultantly, the total demand of capital goods become
80 crores rupees (Column 6) after increment which is gotten from the sum of replacement investment
of 40 crores rupees (Column 4) and net investment of 40 crores rupees (Column 5). The net investment
remains positive until the demand of final goods (Production) is increasing. But when it is started to
reduce then the net investment is negative. In above table, the total production (Column 2) is increasing
in period from t + 1 to t + 4 with an increasing rate, similarly in net investment. Again, in period from
t + 5 to t + 6, it increases with a decreasing rate and net investment is low. The total production falls
in the period from t + 7 to t + 9 and the net investment becomes negative.
The Acceleration theory is shown by the graph in figure 11.1 where in upper part, the total production
curve is increasing with an increasing rate until Y t + 4 period. Again, increases with a decreasing rate
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 93