Page 110 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 110
Unit-12: Demand of Money: Quantity Theory of Money
From the above given example it is clear that by Notes
doubling the quantity of money, price level also
doubles, i.e. from ` 4, it increases to ` 8 and value
of money reduces to half from 1/4 to 1/8. From the
above given example, it is clear that when quantity
of money doubles, then price level also doubles. It
increases from 4 to 8 and value of money decreases
from 1/4 to 1/8.
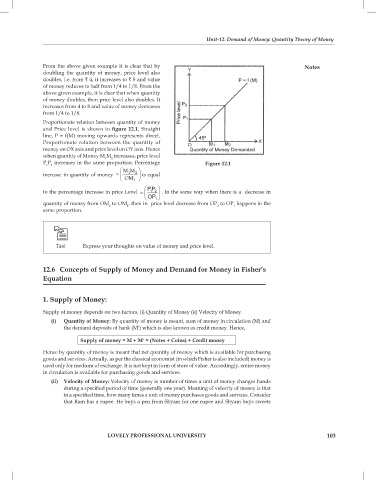
Proportionate relation between quantity of money
and Price level is shown in figure 12.1. Straight
line, P = f(M) moving upwards represents direct.
Proportionate relation between the quantity of
money on OX axis and price level on OY axis. Hence
when quantity of Money M M increases, price level
1
2
P P increases in the same proportion. Percentage Figure 12.1
1 2
MM
increase in quantity of money = 1 2 is equal
OM 1
PP
to the percentage increase in price Level = 12 . In the same way when there is a decrease in
OP 1
quantity of money from OM to OM , then in price level decrease from OP to OP happens in the
1
2
1
2
same proportion.
Task Express your thoughts on value of money and price level.
12.6 Concepts of Supply of Money and Demand for Money in Fisher’s
Equation
1. Supply of Money:
Supply of money depends on two factors, (i) Quantity of Money (ii) Velocity of Money.
(i) Quantity of Money: By quantity of money is meant, sum of money in circulation (M) and
the demand deposits of bank (M′) which is also known as credit money. Hence,
Supply of money = M + M′ = (Notes + Coins) + Credit money
Hence by quantity of money is meant that net quantity of money which is available for purchasing
goods and services. Actually, as per the classical economist (in which Fisher is also included) money is
used only for medium of exchange. It is not kept in form of store of value. Accordingly, entire money
in circulation is available for purchasing goods and services.
(ii) Velocity of Money: Velocity of money is number of times a unit of money changes hands
during a specified period of time (generally one year). Meaning of velocity of money is that
in a specified time, how many times a unit of money purchases goods and services. Consider
that Ram has a rupee. He buys a pen from Shyam for one rupee and Shyam buys sweets
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 103