Page 116 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 116
Unit-12: Demand of Money: Quantity Theory of Money
kR Notes
M = M = C h1 ) c
( −
+
P
1 × 2000
4 1 1 1 500 1 1 1 2 1 1
= 1 2 + 10 1 − 2 = 1 2 + 10 × 2 = 500× 1 2 + 20
2 2
1 × 2000
4 1 + 1 1 − 1 = = 500 1 + 1 × 1 = 500× 2 1 + 1
1 2 10 2 1 2 10 2 1 2 20
2 2
1 1
= 1000 +
2 20
1 1
(in it, 1000 × = `. 500 is with people as currency or legal tender money and 1000 × = `. 50 is
2 20
bank money)
11
= 1000× = `. 550
500
=
20
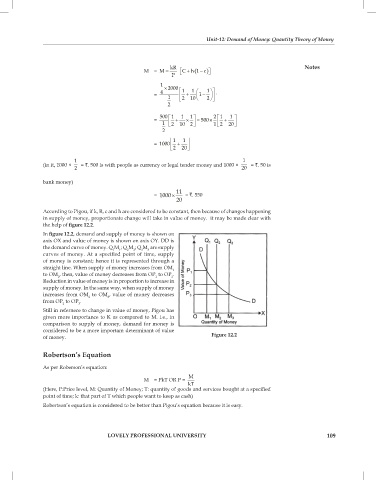
According to Pigou, if k, R, c and h are considered to be constant, then because of changes happening
in supply of money, proportionate change will take in value of money. it may be made clear with
the help of figure 12.2.
In figure 12.2, demand and supply of money is shown on
axis OX and value of money is shown on axis OY. DD is
the demand curve of money. Q M ; Q M ; Q M are supply
2
2
3
3
1
1
curves of money. At a specified point of time, supply
of money is constant; hence it is represented through a
straight line. When supply of money increases from OM 1
to OM , then, value of money decreases from OP to OP .
2
2
1
Reduction in value of money is in proportion to increase in
supply of money. In the same way, when supply of money
increases from OM to OM , value of money decreases
2
3
from OP to OP .
2 3
Still in refernece to change in value of money, Pigou has
given more importance to K as compared to M. i.e., in
comparison to supply of money, demand for money is
considered to be a more important determinant of value
of money. Figure 12.2
Robertson’s Equation
As per Roberson’s equation:
M
M = PkT OR P =
kT
(Here, P:Price level, M: Quantity of Money; T: quantity of goods and services bought at a specified
point of time; k: that part of T which people want to keep as cash)
Robertson’s equation is considered to be better than Pigou’s equation because it is easy.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 109