Page 174 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 174
Unit-18: IS - LM Analysis
combined with the changes occuring in the Notes
prices. So when price level becomes double
then people keep the money in double quantity
in themselves firstly so that their real balances
(or purchasing power) remain constant.
The demand of real balances in economy
depends on two facts: (i)The GDP level and
(ii) Interest rate. The GDP level is the clear
determinor of real balances, because people
keep the money to themselves for purchasing
the goods and services. The high level of GDP
means the high demand of real balances and
vice-versa. The mean of interest rate is the
oppurtunity cost of keeping the money
himself. Because when you keep a fixed
amount of money in cash form then you
have to be deprived from that income gotten
in interest form which you could get if you
had invested this money in bonds purchase.
In other words, the demand of cash balances
are inversely related with interest rate (r) on
a fixed GDP level.
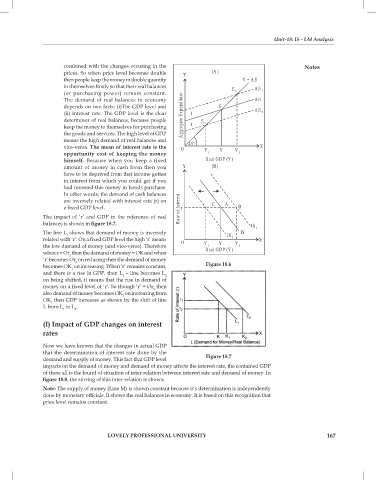
The impact of ‘r’ and GDP in the reference of real
balances is shown in figure 18.7.
The line L shows that demand of money is inversely
1
related with ‘r’. On a fixed GDP level the high ‘r’ means
the low damand of money (and vice-versa). Therefore
when r = Or then the demand of money = OK and when
1
‘r’ becomes Or on reducing then the demand of money
2
becomes OK on increasing. When ‘r’ remains constant, Figure 18.6
1
and there is a rise in GDP, then L – line becomes L
1
2
on being shifted, it means that the rise in demand of
money on a fixed level of ‘r’. So though ‘r’ = Or then
2
also demand of money becomes OK on increasing from
2
OK then GDP increases as shown by the shift of line
1
L from L to L .
2
1
(I) Impact of GDP changes on interest
rates
Now we have known that the changes in actual GDP
that the determination of interest rate done by the
demand and supply of money. This fact that GDP level Figure 18.7
impacts on the demand of money and demand of money affects the interest rate, the contained GDP
of these all is the found of situation of inter-relation between interest rate and demand of money. In
figure 18.8, the stirring of this inter-relation is shown.
Note: The supply of money (Line M) is shown constant because it’s determination is independently
done by monetary officials. It shows the real balances in economy. It is based on this recognition that
price level remains constant.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 167