Page 215 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 215
Macroeconomic Theory
Notes becomes their expectations. Hence when government again adopts such policy then firms increase their
prices for making the expected inflation ineffective so that it does have an influence on production and
employment. In the same way, in expectation for inflation workers demand for more wages and firms
do not give much jobs. In other words, firms and workers make their expectation in labour so that in
the actual rate of unemployment and natural rate, even in short term also, there is no difference.
Task Express your thoughts on rational expectations.
Self Assessment
State whether the following statement are true or false:
7. In long term, trade-off between inflation and employment does not happen.
8. In long term, at natural rate of unemployment, Philips curve is a vertical line.
9. Except for short term there is a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
10. In long term, economy will not be forced to establish at natural unemployment rate.
23.4 Implications of the Phillips Curve Policy
Policy implications of Phillips curve are important. They suggest that without high level of
unemployment, for stopping inflation to what extent can the monetary and fiscal policies be used. In
other words, it guides the officers’ class in this relation that when level of unemployment is given,
then what rate of inflation may be tolerated.
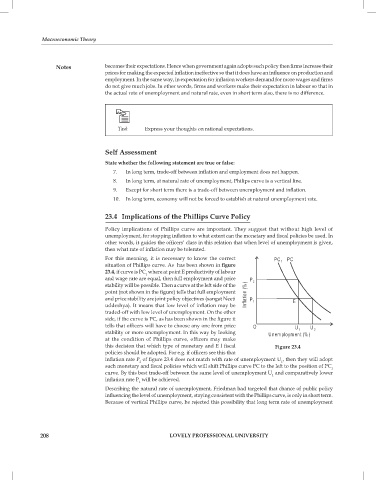
For this meaning, it is necessary to know the correct
situation of Phillips curve. As has been shown in figure
23.4, if curve is PC where at point E productivity of labour
1
and wage rate are equal, then full employment and price
stability will be possible. Then a curve at the left side of the
point (not shown in the figure) tells that full employment
and price stability are joint policy objectives (sangat Neeti
uddeshya). It means that low level of inflation may be
traded-off with low level of unemployment. On the other
side, if the curve is PC, as has been shown in the figure it
tells that officers will have to choose any one from price
stability or more unemployment. In this way by looking
at the condition of Phillips curve, officers may make
this decision that which type of monetary and E l fiscal Figure 23.4
policies should be adopted. For e.g. if officers see this that
inflation rate P of figure 23.4 does not match with rate of unemployment U , then they will adopt
2
1
such monetary and fiscal policies which will shift Phillips curve PC to the left to the position of PC
1
curve. By this best trade-off between the same level of unemployment U and comparatively lower
1
inflation rate P will be achieved.
1
Describing the natural rate of unemployment, Friedman had targeted that chance of public policy
influencing the level of unemployment, staying consistent with the Phillips curve, is only in short term.
Because of vertical Phillips curve, he rejected this possibility that long term rate of unemployment
208 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY