Page 257 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 257
Macroeconomic Theory
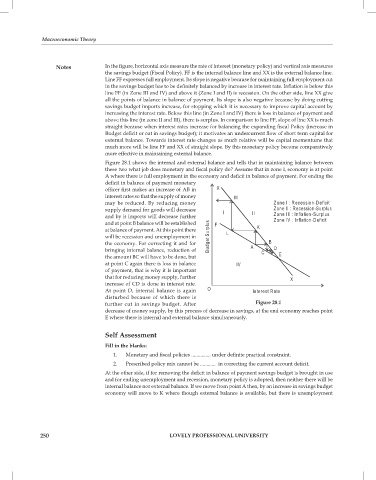
Notes In the figure, horizontal axis measure the rate of interest (monetary policy) and vertical axis measures
the savings budget (Fiscal Policy). FF is the internal balance line and XX is the external balance line.
Line FF expresses full employment. Its slope is negative because for maintaining full employment cut
in the savings budget has to be definitely balanced by increase in interest rate. Inflation is below this
line FF (in Zone III and IV) and above it (Zone I and II) is recession. On the other side, line XX give
all the points of balance in balance of payment. Its slope is also negative because by doing cutting
savings budget imports increase, for stopping which it is necessary to improve capital account by
increasing the interest rate. Below this line (in Zone I and IV) there is loss in balance of payment and
above this line (in zone II and III), there is surplus. In comparison to line FF, slope of line XX is much
straight because when interest rates increase for balancing the expanding fiscal Policy (increase in
Budget deficit or cut in savings budget); it motivates an undercurrent flow of short term capital for
external balance. Towards interest rate changes as much relative will be capital momentums that
much more will be line FF and XX of straight slope. By this monetary policy become comparatively
more effective in maintaining external balance.
Figure 28.1 shows the internal and external balance and tells that in maintaining balance between
these two what job does monetary and fiscal policy do? Assume that in zone I, economy is at point
A where there is full employment in the economy and deficit in balance of payment. For ending the
deficit in balance of payment monetary
officer first makes an increase of AB in
interest rates so that the supply of money
may be reduced. By reducing money
supply demand for goods will decrease
and by it imports will decrease further
and at point B balance will be established
at balance of payment. At this point there
will be recession and unemployment in
the economy. For correcting it and for
bringing internal balance, reduction of
the amount BC will have to be done, but
at point C again there is loss in balance
of payment, that is why it Is important
that for reducing money supply, further
increase of CD is done in interest rate.
At point D, internal balance is again
disturbed because of which there is
further cut in savings budget. After Figure 28.1
decrease of money supply, by this process of decrease in savings, at the end economy reaches point
E where there is internal and external balance simultaneously.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. Monetary and fiscal policies ............... under definite practical constraint.
2. Prescribed policy mix cannot be ............ in correcting the current account deficit.
At the other side, if for removing the deficit in balance of payment savings budget is brought in use
and for ending unemployment and recession, monetary policy is adopted, then neither there will be
internal balance nor external balance. If we move from point A then, by an increase in savings budget
economy will move to K where though external balance is available, but there is unemployment
250 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY