Page 54 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 54
Unit-5: Classical Theory of Employment
for investment will as more and vice versa. Notes
If at certain time the saving is increased from
investment, then the rate of interest will fall.
Investment will increased and then savings
will reduce whenever both is not same at
the level of full employment. It is because
saving considers the increasing function of
interest rate and investment is considering
the decreasing function of interest rate.
The similarity of savings and investment
is shown in figure 5.1 where SS is saving
curve and II is investment curve. Both
curve is intersect each other on E point
where Or is the interest rate and savings
and investment both is equal to the OA. If
investment is increased then investment
curve is sifted right side and become I’I’ Figure 5.1
and OC investment is more than OA savings
at Or interest rate. According to classical
economist, saving curve is on his before situation when investment is increased. Interest rate will
increased for continuing similarity in saving and investment. It shown in figure Or to Or’. At that
interest rate, saving curve investment SS is intersecting on E to investment curve I’I’. Saving and
investment both is equal on OB.
In currency economy the validity of the rule of Say’s is dependent on the classical magnitude principle
which tells that price-level is the function of supply of currency. As Algebra, MV=PT where M,V,P,T
is the supply of currency, the operating velocity of currency, price level and the transaction by
currency. This equation is tells that the total currency-inflation is equal to MV in economies and the
total price of production is PT, if consume that V and T are constant then the supply of currency (M)
is proportionate change in price level (P) by change. It is based on that consumption that currency is
source of exchange.
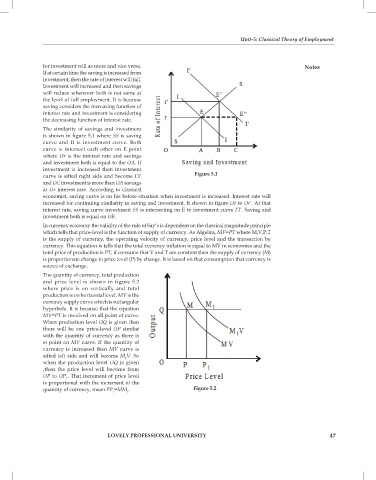
The quantity of currency, total production
and price level is shown in figure 5.2
where price is on vertically and total
production is on horizontal level. MV is the
currency supply curve which is rectangular
hyperbola. It is because that the equation
MV=PT is involved on all point of curve.
When production level OQ is given then
there will be one price-level OP similar
with the quantity of currency as there is
m point on MV curve. If the quantity of
currency is increased then MV curve is
sifted left side and will become M V. So
1
when the production level OQ is given
,then the price level will become from
OP to OP . That increment of price level
1
is proportional with the increment of the
quantity of currency, mean PP =MM . Figure 5.2
1 1
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 47