Page 4 - DECO403_MATHEMATICS_FOR_ECONOMISTS_HINDI
P. 4
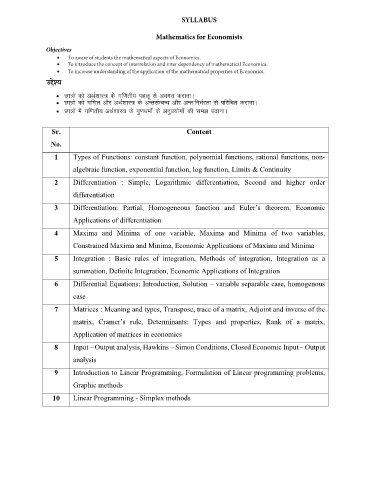
SYLLABUS
Mathematics for Economists
Objectives
• To aware of students the mathematical aspects of Economics.
• To introduce the concept of interrelation and inter dependency of mathematical Economics.
• To increase understanding of the application of the mathematical properties of Economics.
mís';
• Nk=ksa dks vFkZ’kkL= ds xf.krh; igyw ls voxr djkukA
• Nk=ksa dks xf.kr vkSj vFkZ’kkL= ds vUrlZEcU/k vkSj vUr%fuHkZjrk ls ifjfpr djkukA
• Nk=ksa esa xf.krh; vFkZ’kkL= ds xq.k/keksZa ds vuqiz;ksxksa dh le> c<+kukA
Sr. Content
No.
1 Types of Functions: constant function, polynomial functions, rational functions, non-
algebraic function, exponential function, log function, Limits & Continuity
2 Differentiation : Simple, Logarithmic differentiation, Second and higher order
differentiation
3 Differentiation: Partial, Homogeneous function and Euler’s theorem, Economic
Applications of differentiation
4 Maxima and Minima of one variable, Maxima and Minima of two variables,
Constrained Maxima and Minima, Economic Applications of Maxima and Minima
5 Integration : Basic rules of integration, Methods of integration, Integration as a
summation, Definite Integration, Economic Applications of Integration
6 Differential Equations: Introduction, Solution – variable separable case, homogenous
case
7 Matrices : Meaning and types, Transpose, trace of a matrix, Adjoint and inverse of the
matrix, Cramer’s rule, Determinants: Types and properties, Rank of a matrix,
Application of matrices in economics
8 Input – Output analysis, Hawkins – Simon Conditions, Closed Economic Input – Output
analysis
9 Introduction to Linear Programming, Formulation of Linear programming problems,
Graphic methods
10 Linear Programming - Simplex methods