Page 123 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 123
Unit 11: Sectoral Performance I: Agriculture: Growth Productivity Trends and Crop Patterns
(i) Share of Agriculture in the National Income Notes
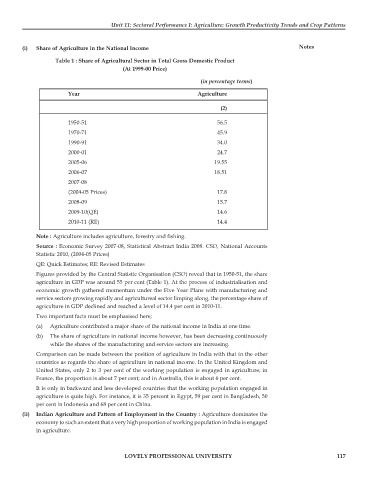
Table 1 : Share of Agricultural Sector in Total Gross Domestic Product
(At 1999-00 Price)
(in percentage terms)
Year Agriculture
(2)
1950-51 56.5
1970-71 45.9
1990-91 34.0
2000-01 24.7
2005-06 19.55
2006-07 18.51
2007-08
(2004-05 Prices) 17.8
2008-09 15.7
2009-10(QE) 14.6
2010-11 (RE) 14.4
Note : Agriculture includes agriculture, forestry and fishing.
Source : Economic Survey 2007-08, Statistical Abstract India 2008. CSO, National Accounts
Statistic 2010, (2004-05 Prices)
QE: Quick Estimates; RE: Revised Estimates
Figures provided by the Central Statistic Organisation (CSO) reveal that in 1950-51, the share
agriculture in GDP was around 55 per cent (Table 1). At the process of industrialisation and
economic growth gathered momentum under the Five Year Plans with manufacturing and
service sectors growing rapidly and agricultureal sector limping along, the percentage share of
agriculture in GDP declined and reached a level of 14.4 per cent in 2010-11.
Two important facts must be emphasised here;
(a) Agriculture contributed a major share of the national income in India at one time.
(b) The share of agriculture in national income however, has been decreasing continuously
while the shares of the manufacturing and service sectors are increasing.
Comparison can be made between the position of agriculture in India with that in the other
countries as regards the share of agriculture in national income. In the United Kingdom and
United States, only 2 to 3 per cent of the working population is engaged in agriculture; in
France, the proportion is about 7 per cent; and in Australia, this is about 6 per cent.
It is only in backward and less developed countries that the working population engaged in
agriculture is quite high. For instance, it is 35 percent in Egypt, 59 per cent in Bangladesh, 50
per cent in Indonesia and 68 per cent in China.
(ii) Indian Agriculture and Pattern of Employment in the Country : Agriculture dominates the
economy to such an extent that a very high proportion of working population in India is engaged
in agriculture.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 117