Page 171 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 171
Unit 14: Rural Credit and Marketing
The organisation of the co-operative credit for short period is briefly outlined here : Notes
Primary Agricultural Credit Society : (PACS) A co-operative credit society, commonly known as the
primary agricultural credit society (PACS) may be started with ten or more persons, normally belonging
to a village. The value of each share is generally nominal so as to enable even the poorest farmer to
become a member. Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PAC S) are the grassroot level arms of the
short-term cooperative credit strucure. PACS deal directly with farmer-borrowers, grant short term
and medium term loans and also undertake distribution and marketing functions.
The management of the society is under an elected body consisting of President, Secretary and
Treasurer. The management is honorary, the only paid member being normally the accountant (in
case the society is large and requires a paid whole-time accountant). Loans are given for short periods,
normally for one year, for carrying out agricultural operations, and the rate of interest is low. Profits
are not distributed as dividend to shareholders but are used for the welfare of the village, in the
construction of a well, or maintenance of the village school, and so on.
The usefulness of PACs has been rising steadily. In 1950-51, they advanced loans worth ` 23 crores;
this rose to ` 200 crores in 1960-61, and to ` 34,520 crores in 2000-01. The PACS have stepped up their
advances to the weaker sections particularly the small and marginal farmers. This progress has been
quite spectacular but not adequate considering the demand for finance from farmers. However, “the
primary credit society has continued to remain the weakest link in the entire co-operative structure.”
Restructuring of PACS : Considerable attention was given during the past few decades to build the
PACS into strong institutions. Such a structure, close to the farmers, is very essential for disbursing
rural credit, particularly to small farmers. A programme was introduced by the Government and RBI
to reorganise and revitalise the primary agricultural credit societies. It was completed in Rajasthan,
Orissa, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Gujarat. In other States, it has not made much
headway.
The number of PACS had come down from 2,12,000 in 1960-61 to 1,61,000 in 1970-71 and 1,06,380 at
the end March 2006 with estimated membership of over 10 crore farmers.
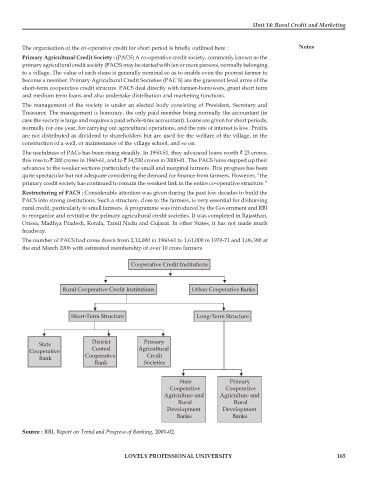
Cooperative Credit Institutions
Rural Cooperative Credit Institutions Urban Cooperative Banks
Short-Term Structure Long-Term Structure
District Primary
State
Central Agricultural
Cooperative
Cooperative Credit
Bank
Bank Societies
State Primary
Cooperative Cooperative
Agriculture and Agriculture and
Rural Rural
Development Development
Banks Banks
Source : RBI, Report on Trend and Progress of Banking, 2001-02.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 165