Page 69 - DECO503_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_AND_FINANCE_ENGLISH
P. 69
Unit 5 : Role of Dynamic Factors : Tastes, Technology and Factors Endowments in Trade
in the terms of trade, in the volume of trade and in the distribution of the gains from trade between Notes
the two nations. The actual result depends on the type and degree of the changes occurring.
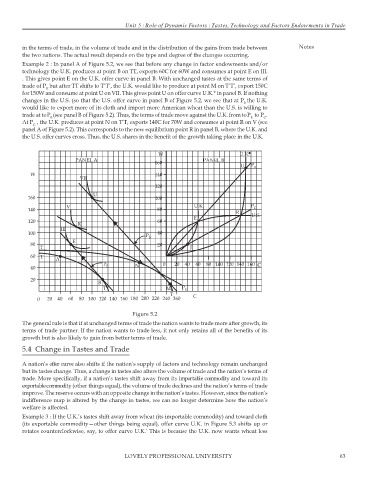
Example 2 : In panel A of Figure 5.2, we see that before any change in factor endowments and/or
technology the U.K. produces at point B on TT, exports 60C for 60W and consumes at point E on III.
. This gives point E on the U.K. offer curve in panel B. With unchanged tastes at the same terms of
trade of P but after TT shifts to T’T’, the U.K. would like to produce at point M on T’T’, export 150C
B
for 150W and consume at point U on VII. This gives point U on offer curve U.K.* in panel B. If nothing
changes in the U.S. (so that the U.S. offer curve in panel B of Figure 5.2, we see that at P the U.K.
B
would like to export more of its cloth and import more American wheat than the U.S. is willing to
trade at toP (see panel B of Figure 5.2). Thus, the terms of trade move against the U.K. from toP to P .
B
B.
G
At P , the U.K. produces at point N on T’T, exports 140C for 70W and consumes at point R on V (see
G
panel A of Figure 5.2). This corresponds to the new equilibrium point R in panel B, where the U.K. and
the U.S. offer curves cross. Thus, the U.S. shares in the benefit of the growth taking place in the U.K.
W U.K.
PANEL A PANEL B
160
U P n
W 140
VII
120
U
160 100
V U.K. P G
140 80
R
E U.S.
120 60
R
III
100 P B 40
E
80 20
T J
60 T
A
P N 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 C
40 B
20
B
T M P G
T C
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260
Figure 5.2
The general rule is that if at unchanged terms of trade the nation wants to trade more after growth, its
terms of trade partner. If the nation wants to trade less, it not only retains all of the benefits of its
growth but is also likely to gain from better terms of trade.
5.4 Change in Tastes and Trade
A nation’s offer curve also shifts if the nation’s supply of factors and technology remain unchanged
but its tastes change. Thus, a change in tastes also alters the volume of trade and the nation’s terms of
trade. More specifically, if a nation’s tastes shift away from its importable commodity and toward its
exportable commodity (other things equal), the volume of trade declines and the nation’s terms of trade
improve. The reserve occurs with an opposite change in the nation’s tastes. However, since the nation’s
indifference map is altered by the change in tastes, we can no longer determine how the nation’s
welfare is affected.
Example 3 : If the U.K.’s tastes shift away from wheat (its importable commodity) and toward cloth
(its exportable commodity—other things being equal), offer curve U.K. in Figure 5.3 shifts up or
rotates counterclockwise, say, to offer curve U.K.’ This is because the U.K. now wants wheat less
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 63