Page 94 - DECO503_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_AND_FINANCE_ENGLISH
P. 94
International Trade and Finance
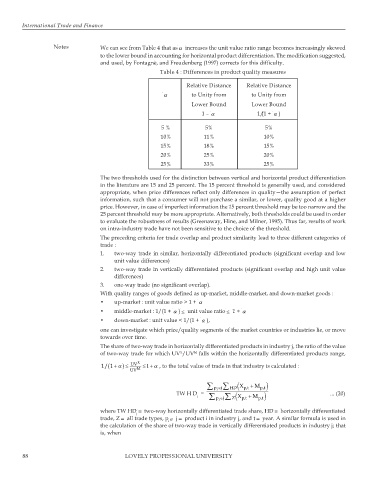
Notes We can see from Table 4 that asα increases the unit value ratio range becomes increasingly skewed
to the lower bound in accounting for horizontal product differentiation. The modification suggested,
and used, by Fontagnè, and Freudenberg (1997) corrects for this difficulty.
Table 4 : Differences in product quality measures
Relative Distance Relative Distance
α to Unity from to Unity from
Lower Bound Lower Bound
1 – α 1/(1 + α )
5 % 5% 5%
10% 11% 10%
15% 18% 15%
20% 25% 20%
25% 33% 25%
The two thresholds used for the distinction between vertical and horizontal product differentiation
in the literature are 15 and 25 percent. The 15 percent threshold is generally used, and considered
appropriate, when price differences reflect only differences in qualitythe assumption of perfect
information, such that a consumer will not purchase a similar, or lower, quality good at a higher
price. However, in case of imperfect information the 15 percent threshold may be too narrow and the
25 percent threshold may be more appropriate. Alternatively, both thresholds could be used in order
to evaluate the robustness of results (Greenaway, Hine, and Milner, 1995). Thus far, results of work
on intra-industry trade have not been sensitive to the choice of the threshold.
The preceding criteria for trade overlap and product similarity lead to three different categories of
trade :
1. two-way trade in similar, horizontally differentiated products (significant overlap and low
unit value differences)
2. two-way trade in vertically differentiated products (significant overlap and high unit value
differences)
3. one-way trade (no significant overlap).
With quality ranges of goods defined as up-market, middle-market, and down-market goods :
up-market : unit value ratio > 1 + α
middle-market : 1/(1 + α ) ≤ unit value ratio ≤ 1 + α
down-market : unit value < 1/(1 + α ),
one can investigate which price/quality segments of the market countries or industries lie, or move
towards over time.
The share of two-way trade in horizontally differentiated products in industry j, the ratio of the value
X
M
of two-way trade for which UV /UV falls within the horizontally differentiated products range,
1/ ( +1 α ) ≤ UV X ≤1+ α , to the total value of trade in that industry is calculated :
UV M
∑ i p ∈ j∑ HD ( X p,t + M p,t )
TW H D = ... (20)
j ∑ i p ∈ j∑ Z ( X p,t + M p,t )
where TW HD ≡ two-way horizontally differentiated trade share, HD ≡ horizontally differentiated
j
trade, Z ≡ all trade types, p ∈ j ≡ product i in industry j, and t ≡ year. A similar formula is used in
i
the calculation of the share of two-way trade in vertically differentiated products in industry j; that
is, when
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY