Page 101 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 101
Unit 8 : Test Construction
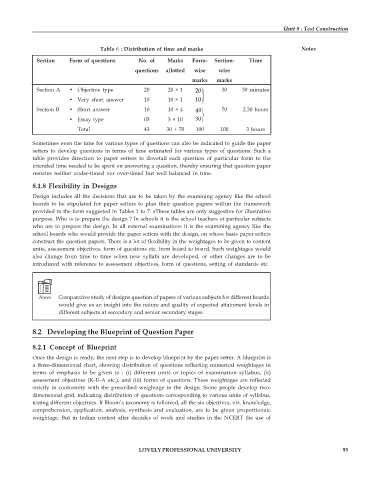
Table 6 : Distribution of time and marks Notes
Section Form of questions No. of Marks Form- Section- Time
questions allotted wise wise
marks marks
Section A • Objective type 20 20 × 1 20⎫ 30 30 minutes
• Very short answer 10 10 × 1 10 ⎬ ⎭
Section B • Short answer 10 10 × 4 40 ⎫ 70 2.30 hours
• Essay type 03 3 × 10 30 ⎬ ⎭
Total 43 30 + 70 100 100 3 hours
Sometimes even the time for various types of questions can also be indicated to guide the paper
setters to develop questions in terms of time estimated for various types of questions. Such a
table provides direction to paper setters to dovetail each question of particular form to the
intended time needed to be spent on answering a question, thereby ensuring that question paper
remains neither under-timed nor over-timed but well balanced in time.
8.1.8 Flexibility in Designs
Design includes all the decisions that are to be taken by the examining agency like the school
boards to be stipulated for paper setters to plan their question papers within the framework
provided in the form suggested in Tables 1 to 7. sThese tables are only suggestive for illustrative
purpose. Who is to prepare the design ? In schools it is the school teachers of particular subjects
who are to prepare the design. In all external examinations it is the examining agency like the
school boards who would provide the paper setters with the design, on whose basis paper setters
construct the question papers. There is a lot of flexibility in the weightages to be given to content
units, assessment objectives, form of questions etc. from board to board. Such weightages would
also change from time to time when new syllabi are developed, or other changes are to be
introduced with reference to assessment objectives, form of questions, setting of standards etc.
Comparative study of designs question of papers of various subjects for different boards
would give us an insight into the nature and quality of expected attainment levels in
different subjects at secondary and senior secondary stages.
8.2 Developing the Blueprint of Question Paper
8.2.1 Concept of Blueprint
Once the design is ready, the next step is to develop blueprint by the paper setter. A blueprint is
a three-dimensional chart, showing distribution of questions reflecting numerical weightages in
terms of emphasis to be given to : (i) different units or topics of examination syllabus, (ii)
assessment objectives (K-U-A etc.), and (iii) forms of questions. These weightages are reflected
strictly in conformity with the prescribed weightage in the design. Some people develop two-
dimensional grid, indicating distribution of questions corresponding to various units of syllabus,
testing different objectives. If Bloom’s taxonomy is followed, all the six objectives, viz. knowledge,
comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation, are to be given proportionate
weightage. But in Indian context after decades of work and studies in the NCERT the use of
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 95