Page 120 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 120
Educational Measurement and Evaluation
Notes where RH = the number of students attempting the item correctly from the higher group
(10); RL = the number of students attempting the item correctly from the lower group (4);
NH = the number of students in the High or Low group (27).
10 – 4 6 2
D1 = = = = 0.22
27 27 9
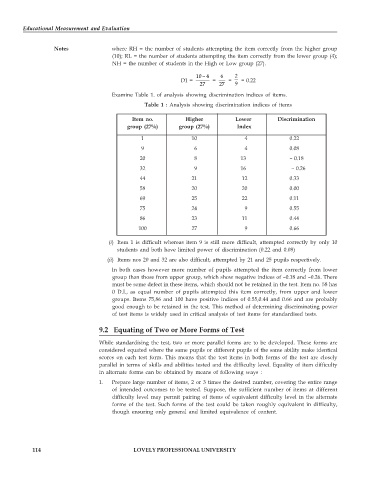
Examine Table 1. of analysis showing discrimination indices of items.
Table 1 : Analysis showing discrimination indices of items
Item no. Higher Lower Discrimination
group (27%) group (27%) Index
1 10 4 0.22
9 6 4 0.08
20 8 13 – 0.18
32 9 16 – 0.26
44 21 12 0.33
58 20 20 0.00
69 25 22 0.11
75 24 9 0.55
86 23 11 0.44
100 27 9 0.66
(i) Item 1 is difficult whereas item 9 is still more difficult, attempted correctly by only 10
students and both have limited power of discrimination (0.22 and 0.08)
(ii) Items nos 20 and 32 are also difficult, attempted by 21 and 25 pupils respectively.
In both cases however more number of pupils attempted the item correctly from lower
group than those from upper group, which show negative indices of –0.18 and –0.26. There
must be some defect in these items, which should not be retained in the test. Item no. 58 has
0 D.I., as equal number of pupils attempted this item correctly, from upper and lower
groups. Items 75,86 and 100 have positive indices of 0.55,0.44 and 0.66 and are probably
good enough to be retained in the test. This method of determining discriminating power
of test items is widely used in critical analysis of test items for standardised tests.
9.2 Equating of Two or More Forms of Test
While standardising the test, two or more parallel forms are to be developed. These forms are
considered equated where the same pupils or different pupils of the same ability make identical
scores on each test form. This means that the test items in both forms of the test are closely
parallel in terms of skills and abilities tested and the difficulty level. Equality of item difficulty
in alternate forms can be obtained by means of following ways :
1. Prepare large number of items, 2 or 3 times the desired number, covering the entire range
of intended outcomes to be tested. Suppose, the sufficient number of items at different
difficulty level may permit pairing of items of equivalent difficulty level in the alternate
forms of the test. Such forms of the test could be taken roughly equivalent in difficulty,
though ensuring only general and limited equivalence of content.
114 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY