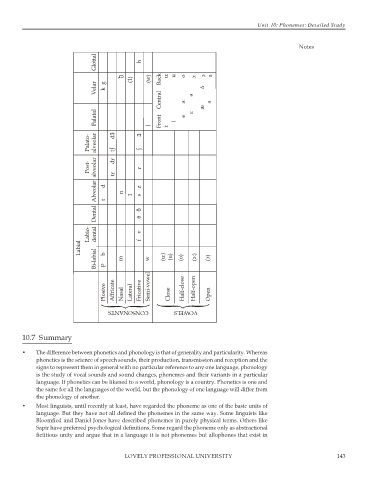
Page 149 - DENG504_LINGUISTICS
P. 149
Unit 10: Phonemes: Detailed Study
Notes
Glottal h :c c
Velar k g (1) (w) Back Central u: u :e o e ∆ a
Palatal e ε æ a
j Front i: i
Palato- alveolar d3 t∫ 3 ∫
Post- alveolar tr dr r
Alveolar t d n 1 s z
Dental ð θ
Labio- dental f v
Labial
Bi-labial p b m w (u:) (u) (o) c c ( )
( :)
Plosive Affricate Nasal Lateral Fricative CONSONANTS Semi-vowel Close Half-close Half-open VOWELS Open
10.7 Summary
• The difference between phonetics and phonology is that of generality and particularity. Whereas
phonetics is the science of speech sounds, their production, transmission and reception and the
signs to represent them in general with no particular reference to any one language, phonology
is the study of vocal sounds and sound changes, phonemes and their variants in a particular
language. If phonetics can be likened to a world, phonology is a country. Phonetics is one and
the same for all the languages of the world, but the phonology of one language will differ from
the phonology of another.
• Most linguists, until recently at least, have regarded the phoneme as one of the basic units of
language. But they have not all defined the phonemes in the same way. Some linguists like
Bloomfied and Daniel Jones have described phonemes in purely physical terms. Others like
Sapir have preferred psychological definitions. Some regard the phoneme only as abstractional
fictitious unity and argue that in a language it is not phonemes but allophones that exist in
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 143