Page 370 - DENG504_LINGUISTICS
P. 370
Linguistics
Notes Instrument with, by
Causative by
Result to, in, into
Source from
Goal to
Location in, at, on, near, around, beyond.
This is only a rough outline. Other cases are to be added and have, in fact, already been added.
Fillmore has recently modified his theory and his terminology. But there are many difficulties ahead,
both in establishing what cases are required and in the relationship between the deep grammar and
the surface grammar. Nevertheless the credit goes to TG that it has stimulated such speculation.
28.5 Stratificational Grammar
Stratificational Grammar is associated with the name of Sidney Lamb. According to Sidney Lamb,
language does not have only two levels of deep and surface structures but a series of levels or strata,
each with a different kind of structure. This grammar has come to be known as Stratificational
grammar as one of its chief features is its treatment of linguistic structure as comprising several
structural layers called strata by Lamb. ‘A language is a complex network of sound-meaning
relationships. These relationships can be analysed in terms of a series of code-like systems. Each of
these systems has its own syntax or tactics.’
According to Lamb, therefore, all natural languages may be said to have three major strata : Semology,
Grammar, and Phonology. Semology is concerned with meaning and phonology with speech.
Grammar is a ‘link’ between the two.
In stratificational grammar a sentence is realized as a string of sounds, a tree of morphemes and a
constellation of meanings. The basic relationship in this model is that of representation of realization.
It links the elements of one stratum with those of the stratum next below. Lamb’s Outline of
Stratificational Grammar (Georgetown University Press, Washington D.C., 1966) gives the features of
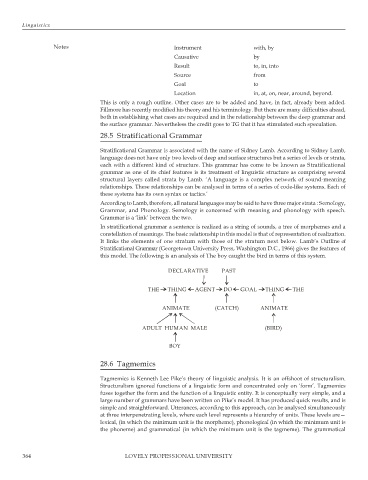
this model. The following is an analysis of The boy caught the bird in terms of this system.
DECLARATIVE PAST
THE THING AGENT DO GOAL THING THE
ANIMATE (CATCH) ANIMATE
ADULT HUMAN MALE (BIRD)
BOY
28.6 Tagmemics
Tagmemics is Kenneth Lee Pike’s theory of linguistic analysis. It is an offshoot of structuralism.
Structuralism ignored functions of a linguistic form and concentrated only on ‘form’. Tagmemics
fuses together the form and the function of a linguistic entity. It is conceptually very simple, and a
large number of grammars have been written on Pike’s model. It has produced quick results, and is
simple and straightforward. Utterances, according to this approach, can be analysed simultaneously
at three interpenetrating levels, where each level represents a hierarchy of units. These levels are—
lexical, (in which the minimum unit is the morpheme), phonological (in which the minimum unit is
the phoneme) and grammatical (in which the minimum unit is the tagmeme). The grammatical
364 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY