Page 53 - DENG504_LINGUISTICS
P. 53
Unit 4: Phonetics: Speech Mechanisms-Places and Manners of Articulation
modified in any of these areas in a variety of ways. Such modification results from some kind of Notes
interference with the movement of the air stream. The most important roles are played by the
vocal cords, soft palate, tongue, lips, teeth and nose.
Now we shall discuss the role of each speech organ in the production of speech:
1. The Diaphragm and Lungs: The diaphragm is situated in the human body below the lungs
and controls the expansion and contraction of the lungs in breathing. It is involved in the
production of chest-pulses on which the division of syllables is based. The lungs serve as a
source for air, which passes upward through the wind-pipe and larynx consisting of the vocal
cords on the mouth or both, and comes outwards. The source of energy for the production of
speech is generally the air-stream coming out of the lungs. It is certainly so in the case of all
sounds used in Punjabi, Hindi, and English.
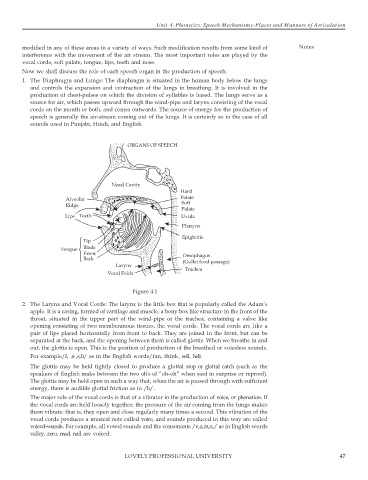
ORGANS OF SPEECH
Nasal Cavity
Hard
Alveolar Palate
Ridge Soft
Palate
Lips Teeth Uvula
Pharynx
Epiglottis
Tip
Tongue Blade
Front Oesophagus
Back (Gullet food passage)
Larynx Trachea
Vocal Folds
Figure 4.1
2. The Larynx and Vocal Cords: The larynx is the little box that is popularly called the Adam’s
apple. It is a casing, formed of cartilage and muscle, a bony box like structure in the front of the
throat, situated in the upper part of the wind-pipe or the trachea, containing a valve like
opening consisting of two memberanous tissues, the vocal cords. The vocal cords are like a
pair of lips placed horizontally from front to back. They are joined in the front, but can be
separated at the back, and the opening between them is called glottis. When we breathe in and
out, the glottis is open. This is the position of production of the breathed or voiceless sounds.
For example/f, θ ,s,h/ as in the English words/fan, think, sell, hell.
The glottis may be held tightly closed to produce a glottal stop or glottal catch (such as the
speakers of English make between the two oh’s of “oh-oh” when said in surprise or reproof).
The glottis may be held open in such a way that, when the air is passed through with sufficient
energy, there is audible glottal friction as in /h/.
The major role of the vocal cords is that of a vibrator in the production of voice, or phonation. If
the vocal cords are held loosely together, the pressure of the air coming from the lungs makes
them vibrate: that is, they open and close regularly many times a second. This vibration of the
vocal cords produces a musical note called voice, and sounds produced in this way are called
voiced-sounds. For example, all vowel sounds and the consonants /v,z,m,n,/ as in English words
valley, zero, mad, nail are voiced.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 47