Page 82 - DMTH404_STATISTICS
P. 82
Statistics
Notes
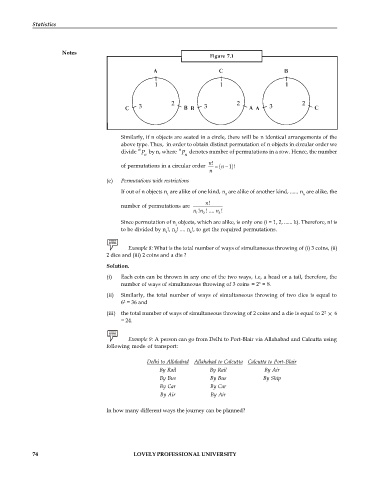
Figure 7.1
Similarly, if n objects are seated in a circle, there will be n identical arrangements of the
above type. Thus, in order to obtain distinct permutation of n objects in circular order we
n n
divide P by n, where P denotes number of permutations in a row. Hence, the number
n n
! n
of permutations in a circular order = (n - ) 1 !
n
(e) Permutations with restrictions
If out of n objects n are alike of one kind, n are alike of another kind, ...... n are alike, the
1 2 k
! n
number of permutations are
n
n 1 !n 2 ! .... !
k
Since permutation of n objects, which are alike, is only one (i = 1, 2, ...... k). Therefore, n! is
i
to be divided by n !, n ! .... n !, to get the required permutations.
1 2 k
Example 8: What is the total number of ways of simultaneous throwing of (i) 3 coins, (ii)
2 dice and (iii) 2 coins and a die ?
Solution.
(i) Each coin can be thrown in any one of the two ways, i.e, a head or a tail, therefore, the
number of ways of simultaneous throwing of 3 coins = 2 = 8.
3
(ii) Similarly, the total number of ways of simultaneous throwing of two dice is equal to
6 = 36 and
2
(iii) the total number of ways of simultaneous throwing of 2 coins and a die is equal to 2 6
2
= 24.
Example 9: A person can go from Delhi to Port-Blair via Allahabad and Calcutta using
following mode of transport:
to
to
Delhi Allahabad Allahabad Calcutta Calcutta Port -Blair
to
By Rail By Rail By Air
By Bus By Bus By Ship
By Car By Car
By Air By Air
In how many different ways the journey can be planned?
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY