Page 12 - DCOM101_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 12
Financial Accounting-I
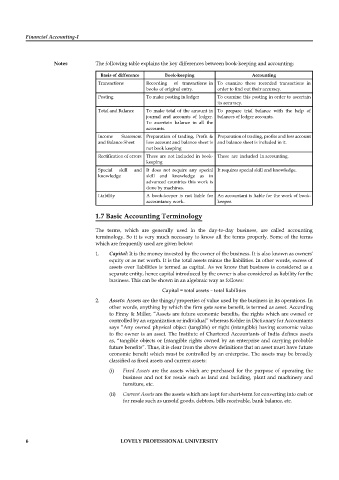
Notes The following table explains the key differences between book-keeping and accounting:
Basis of difference Book-keeping Accounting
Transactions Recording of transactions in To examine these recorded transactions in
books of original entry. order to find out their accuracy.
Posting To make posting in ledger To examine this posting in order to ascertain
its accuracy.
Total and Balance To make total of the amount in To prepare trial balance with the help of
journal and accounts of ledger. balances of ledger accounts.
To ascertain balance in all the
accounts.
Income Statement Preparation of trading, Profit & Preparation of trading, profits and loss account
and Balance Sheet loss account and balance sheet is and balance sheet is included in it.
not book keeping
Rectification of errors These are not included in book- These are included in accounting.
keeping
Special skill and It does not require any special It requires special skill and knowledge.
knowledge skill and knowledge as in
advanced countries this work is
done by machines.
Liability A book-keeper is not liable for An accountant is liable for the work of book-
accountancy work. keeper.
1.7 Basic Accounting Terminology
The terms, which are generally used in the day-to-day business, are called accounting
terminology. So it is very much necessary to know all the terms properly. Some of the terms
which are frequently used are given below:
1. Capital: It is the money invested by the owner of the business. It is also known as owners’
equity or as net worth. It is the total assets minus the liabilities. In other words, excess of
assets over liabilities is termed as capital. As we know that business is considered as a
separate entity, hence capital introduced by the owner is also considered as liability for the
business. This can be shown in an algebraic way as follows:
Capital = total assets – total liabilities
2. Assets: Assets are the things/properties of value used by the business in its operations. In
other words, anything by which the firm gets some benefit, is termed as asset. According
to Finny & Miller, “Assets are future economic benefits, the rights which are owned or
controlled by an organization or individual” whereas Kohler in Dictionary for Accountants
says “Any owned physical object (tangible) or right (intangible) having economic value
to the owner is an asset. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India defines assets
as, “tangible objects or Intangible rights owned by an enterprise and carrying probable
future benefits”. Thus, it is clear from the above definitions that an asset must have future
economic benefit which must be controlled by an enterprise. The assets may be broadly
classified as fixed assets and current assets:
(i) Fixed Assets are the assets which are purchased for the purpose of operating the
business and not for resale such as land and building, plant and machinery and
furniture, etc.
(ii) Current Assets are the assets which are kept for short-term for converting into cash or
for resale such as unsold goods, debtors, bills receivable, bank balance, etc.
6 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY