Page 183 - DCOM106_COMPANY_LAW
P. 183
Company Law
Notes Desirable behaviors embody the beliefs and culture of the organization as defined and enacted
through not only strategy but also corporate value statements, mission statements, business
principles, rituals, and structures. Desirable behaviors are different in every enterprise. Behaviors,
not strategies, create value. For example, Johnson & Johnson relied on autonomous business
units to create shareholder value for nearly a hundred years. Eventually, however, customers
insisted that they wanted to deal with J&J not a set of individual J&J operating companies.
Accordingly, J&J’s well-known corporate credo has evolved to specify desirable behaviors such
as lowering the cost of its products to customers, creating mechanisms for better understanding
the unique needs of individual customers, and transferring employees across J&J companies to
enhance individual careers and help them identify with the corporation.
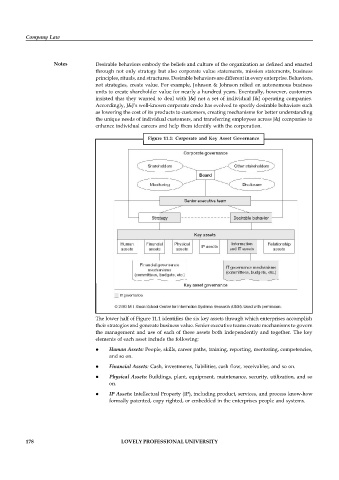
Figure 11.1: Corporate and Key Asset Governance
The lower half of Figure 11.1 identifies the six key assets through which enterprises accomplish
their strategies and generate business value. Senior executive teams create mechanisms to govern
the management and use of each of these assets both independently and together. The key
elements of each asset include the following:
Human Assets: People, skills, career paths, training, reporting, mentoring, competencies,
and so on.
Financial Assets: Cash, investments, liabilities, cash flow, receivables, and so on.
Physical Assets: Buildings, plant, equipment, maintenance, security, utilization, and so
on.
IP Assets: Intellectual Property (IP), including product, services, and process know-how
formally patented, copy righted, or embedded in the enterprises people and systems.
178 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY